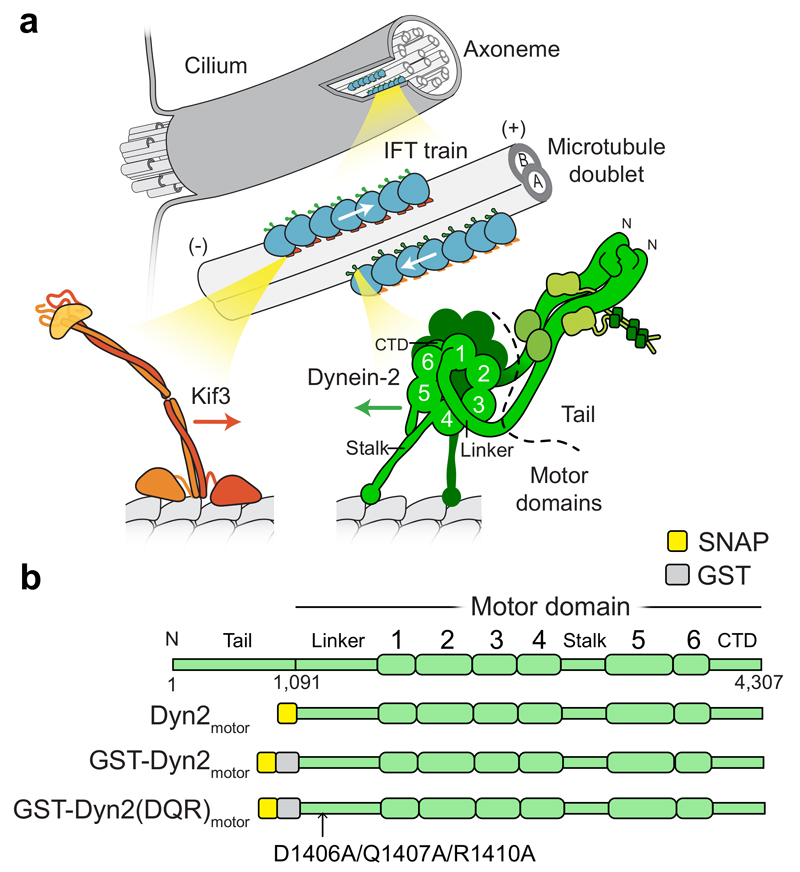
Figure 1. Intraflagellar transport motors and constructs used in this study.
(a) Series of enlargements depicting the cilium; its constituent microtubule doublets; IFT trains that move cargoes along the microtubule doublets; and the motors that power train movement. (+) and (-) indicate microtubule polarity. Kinesin-II family member Kif3 powers transport towards the ciliary tip. Dynein-2 powers transport towards the cell body, functioning as a homodimer of two heavy chains and several associated subunits. Each heavy chain contains a motor domain including the linker, six AAA+ modules (1-6), C-terminal domain (CTD), and microtubule-binding stalk.
(b) Linear diagrams of the dynein-2 heavy chain and key motor domain constructs used in this study.