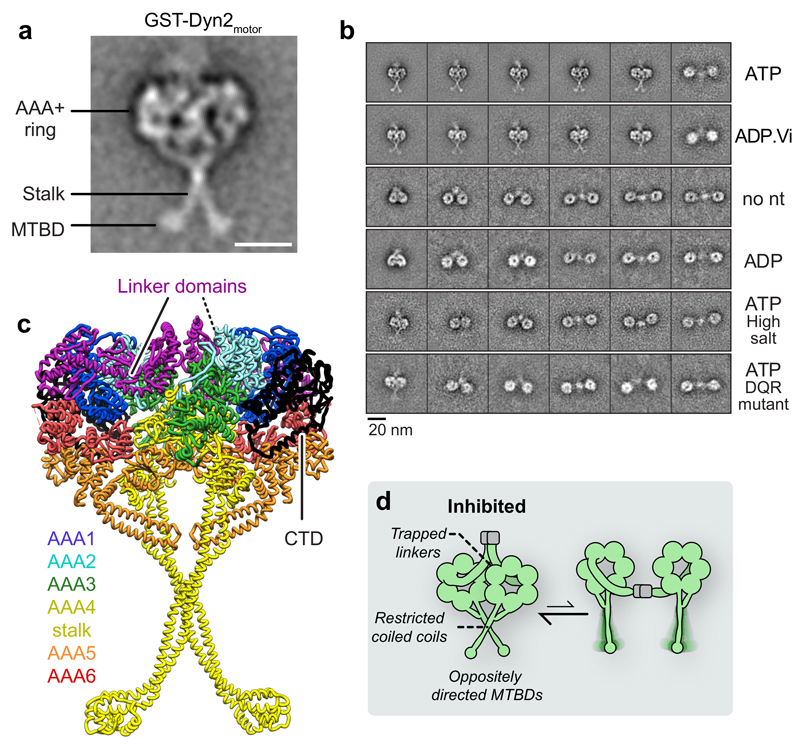
Figure 4. Dynein-2’s linker and stalk are trapped within a novel motor-motor interface.
(a) EM class average of GST-Dyn2motor in 1 mM ATP. Subdomains are labeled. Scale bar; 10 nm. The AAA+ rings are closely apposed and stalks are crossed. MTBD; microtubule-binding domain.
(b) Example class averages of GST-Dyn2motor and GST-Dyn2(DQR)motor in different nucleotide and salt conditions. Nucleotide concentration; 1 mM. High salt; 500 mM KCl. GST-Dyn2motor molecules are predominantly stacked in ATP and ADP.Vi, while separated in other conditions. Stalks are not resolved in separated class averages owing to flexibility. Mutation of three amino acids within the linker (D1406A/Q1407A/R1410A; DQR mutant) almost abolishes stacking. See also Supplementary Fig. 2.
(c) Atomic model for the stacked arrangement of dynein-2 dimers in ATP an ADP.Vi conditions, derived from monomer crystal structure PDB 4RH7 31 as depicted in Supplementary Video 3. Linker domains and C-terminal domain (CTD) are indicated. AAA+ modules and stalk are colored according to the code.
(d) Schematic illustrating proposed structural mechanism of inhibition in stacked dynein-2 dimers (left), in equilibrium with the separated form (right).