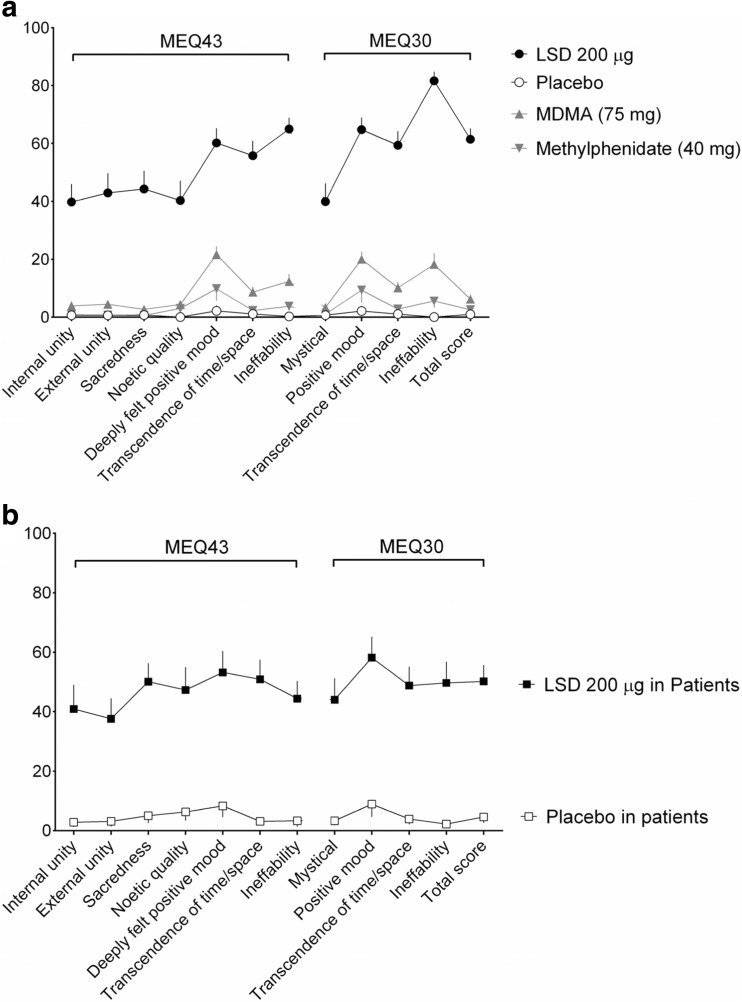
Fig. 1.
Effects of LSD on the Mystical Experience Questionnaire (MEQ). a In the present study in healthy subjects, LSD (200 μg) significantly increased scores on all scales of the MEQ43 and MEQ30 compared with placebo (Table 1). The data are expressed as the mean ± SEM in 16 subjects. For comparison, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA; 75 mg) and methylphenidate (40 mg) produced small increases in MEQ ratings in 30 different participants in another study in the same research setting (Schmid et al. 2014). b Effects of LSD on the MEQ in patients with anxiety in the context of life-threatening illness. The data were analyzed identically to the data that were obtained in the present study. The study and patient characteristics have been previously published in detail (Diesch 2015; Gasser et al. 2014; Gasser et al. 2015; Schmid et al. 2014). Similar to the present study, the MEQ was administered on the day after LSD (200 μg) or active placebo (25 μg LSD) administration and was embedded into the larger 100-item States of Consciousness Questionnaire (SOCQ; Griffiths et al. 2006). The patient data are expressed as the mean ± SEM in 11 subjects for LSD (200 μg, same formulation as in the present study) and four subjects for placebo. On the 43- and 30-item versions of the MEQ, LSD (200 μg) increased MEQ rating scores in the patients in the therapeutic setting (b) to a similar extent as in the healthy subjects in the present study (a). Notably, the placebo response (a very low dose of LSD of 25 μg was used as the active placebo) in the patients was small (b), which was also similar to the response in healthy subjects in the present study (a)