Fig. (3).
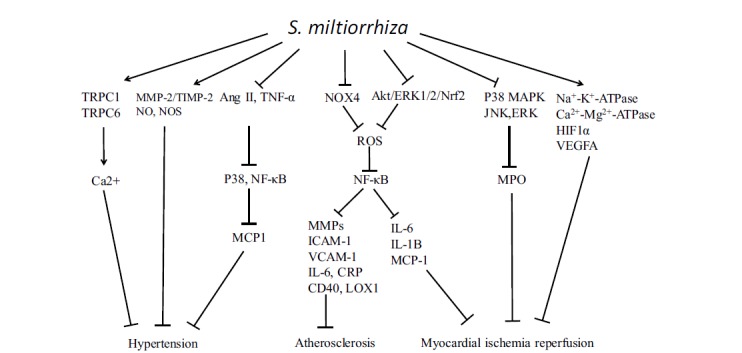
The revealed pathways targeted by S. miltiorrhiza. S. miltiorrhiza could downregulate the levels of Nox4, ROS, NF-κB, MMPs, ICAM-1, VCAM-1, IL-6, CRP, CD40, and LOX1, which contributes to inhibition of atherosclerosis. S. miltiorrhiza suppresses P38MAPK/JNK/ERK pathway, and activates Na+-K+-ATPase, Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase, HIF1α and VEGFA, which facilitates improvement of CVD. Further, S. miltiorrhiza upregulates TRPC1/TRPC6/Ca2+, MMP-2/TIMP-2, NO and NOS expression, and inhibits Ang II, TNF-α/P38/NF-κB/MCP1 pathways, which contribute to the inhibition of hypertension.
