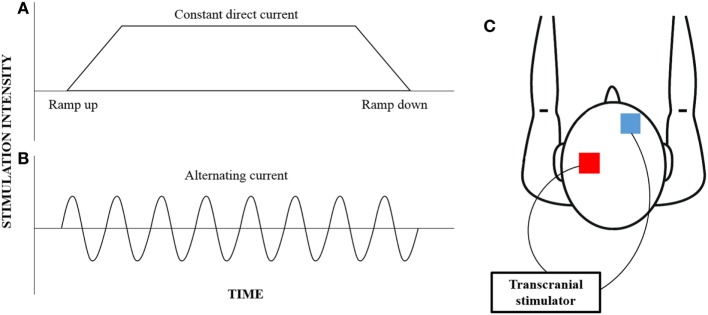
Figure 1.
An illustration of the different current waveforms that can be provided by transcranial stimulation. Convention transcranial direct current stimulation (A) provides constant current that begins with a ramp-up phase and ends with a ramp-down phase; however, transcranial alternating current stimulation (B) provides a rhythmic waveform that can be customized to target specific neural oscillations. While the electrodes (red—anode; blue—cathode) are typically placed over the motor cortex and the contralateral supraorbital region (C), the electrode montage can be customized to target any cortical region of interest.