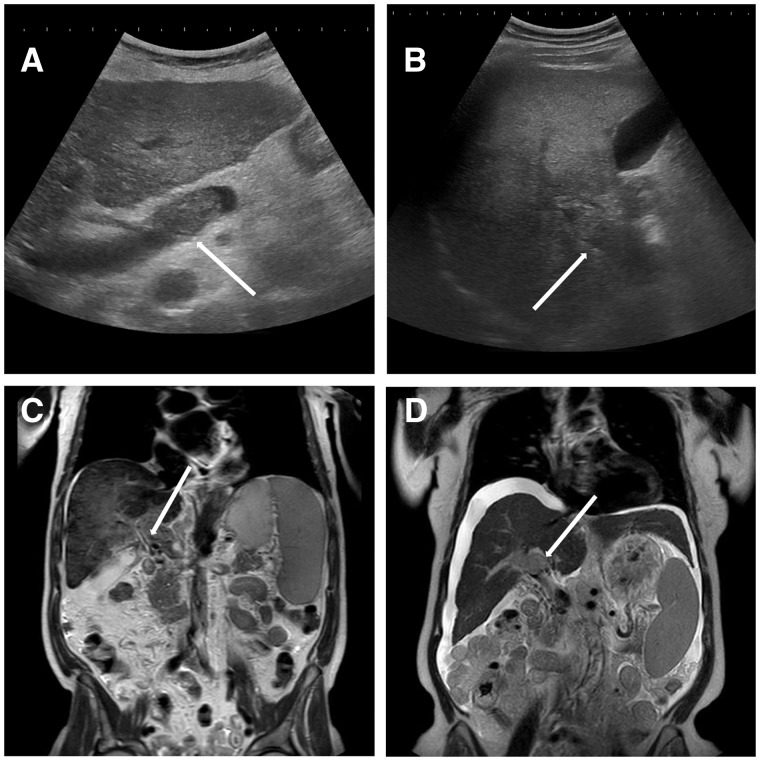
Figure 1.
Imaging findings of portal vein thrombosis. (A) An ultrasound study of the liver of a female patient with liver cirrhosis Child-Pugh C, which revealed echogenic thrombosis (arrow) in the lumen of portal vein trunk. Upon further investigation, a hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was diagnosed. (B) Another ultrasound study of the liver of a male patient with liver cirrhosis Child-Pugh B also revealing echogenic thrombosis (arrow) in the lumen of the portal vein trunk and intrahepatic right portal branch. Further investigation showed a mutation in JAK2-V617F-gene. (C) A CT scan of a male patient with alcohol-related liver cirrhosis and portal cavernoma (arrow). (D) A CT scan of a female patient with chronic hepatitis C infection and development of portal vein thrombosis due to HCC (arrow).