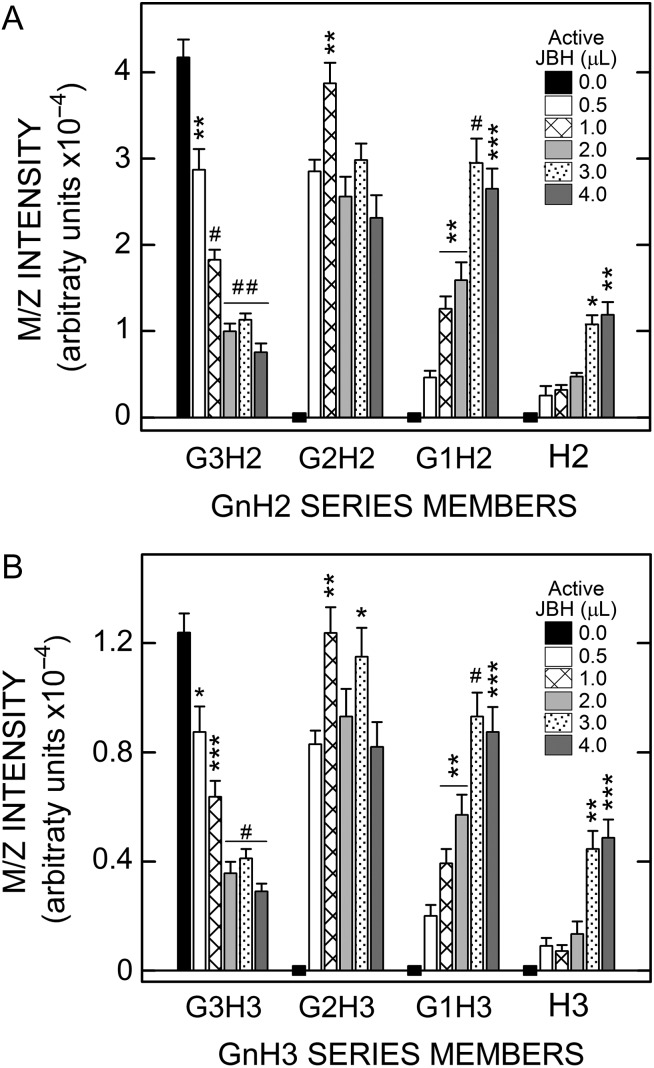
Fig. 5.
Dose-dependent JBH treatment converts larger GnHnoligos from SeHAS HA to smaller GnHn species indicating sequential GlcNAc linkages. Aliquots (0.75 µL) of Wash 3 were incubated at 30°C overnight with 4.0 µL of JBH as a combination of active and heat-inactivated enzyme. Samples had no active JBH (black bars; 0 µL active enzyme; 4.0 µL inactive enzyme) or increasing amounts of active JBH (µL: 0.5, white bars; 1.0, cross-lined bars; 2.0, light gray bars; 3.0, stippled bars; 4.0, dark gray bars), and decreasing amounts of inactive JBH, as described in Methods. Members of the G0–3H2 (A) and G0–3H3 (B) series were analyzed to monitor decreases or increases in each member as a function of increasing active JBH concentration. Significant differences for G3H2,3, assessed by paired Student t-tests, between samples with varying JBH activity vs. inactive JBH, are indicated for two independent experiments; values are the mean intensity ± SEM (n = 8): *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005; ***P < 0.0005; #P < 0.00005; ##P < 0.000005. Since starting values for G1,2H2,3 and H2 and H3 were zero (denoted by zero-line black rectangles), P values for the samples with 1.0–4.0 µL active JBH were compared to the sample with 0.5 µL, the lowest active JBH dose.