FIG. 2.
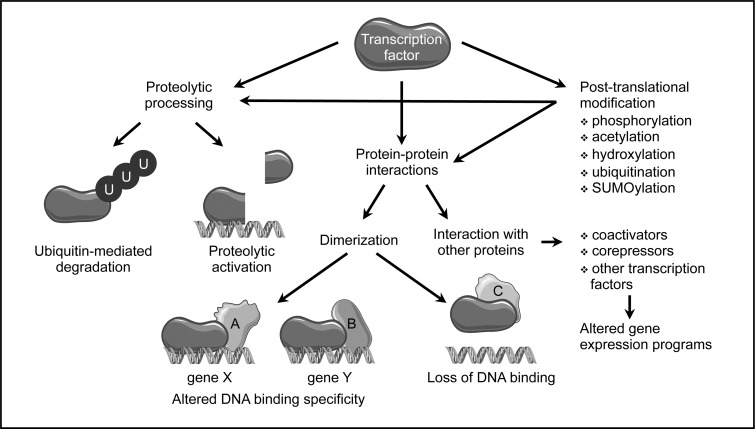
Post-translational regulation of transcription factor activity. Besides regulation on the level of expression as well as RNA splicing and stability, transcription factor activity can be extensively modulated on the protein level. Ubiquitination usually leads to degradation; targeted proteolytic processing of an inactive precursor can result in activation. Dimerization with other transcriptional regulators can alter DNA binding specificity and, thus, target gene selection or even prevent binding. Furthermore, changes in interactions with other, unrelated transcription factors or coactivators and -repressors can alter gene expression programs. Various covalent post-translational modifications of single amino acid residues can affect all the above-described processes.