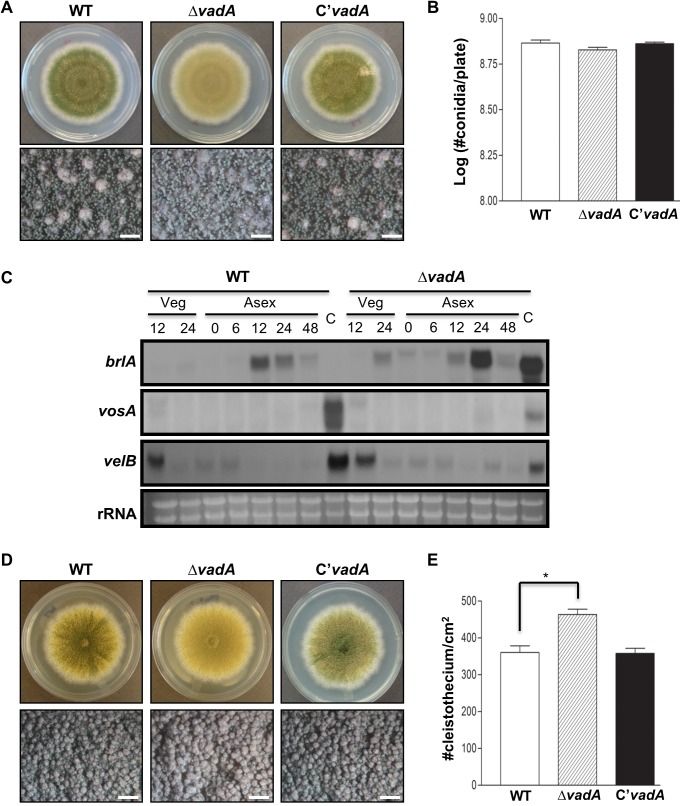
Fig 2. Developmental phenotypes of the ΔvadA mutant.
(A) Colony photographs of WT (FGSC4), ΔvadA (THS33.1), and the complemented (THS34.1) strains point inoculated on solid MM and grown for four days (top and bottom panels). The bottom panel shows close-up views of the center of the plates. (bar = 0.5 mm) (B) Quantitative analysis of conidiospore formation of the strains shown in (A). (C) Northern blot for brlA, vosA, and velB mRNAs in WT (FGSC4) and ΔvadA (THS33.1) strains in vegetative growth (Veg) and post-asexual developmental induction (Asex). Numbers indicate the time (h) of incubation after induction of asexual development. Equal loading of total RNA was confirmed by ethidium bromide staining of rRNA. (D) Colony photographs of WT (FGSC4), ΔvadA (THS33.1), and the complemented (THS34.1) strains point inoculated on solid SM and grown for five days (top and bottom panels). The bottom panel shows close-up views of the center of the plates. (bar = 0.5 mm) (E) Quantitative analysis of cleistothecia formation of strains shown in (A) (* P < 0.05).