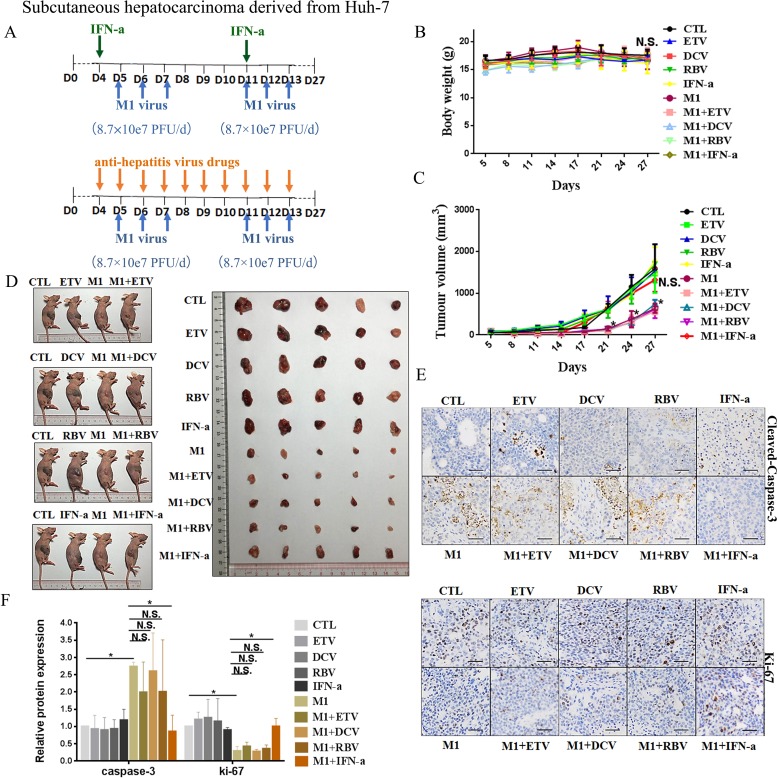
Figure 4. IFN-α attenuates anti-tumor activity of M1 virus invivo subcutaneous Huh-7tumors.
(A) Nude mice (NU/NU) bearing subcutaneous Huh-7 tumors were treated with vehicle ETV (75 μg/kg/day, i.p.), DAC (15 mg/kg/day, i.p.), RBV (15 mg/kg/day, i.p.) IFN-α (35μg/kg/week, s.c.), M1 virus (8.7 × 107 PFU/day, i.v.), M1 virus and anti-hepatitis virus drugs. i.p.intraperitoneal injection, i.v., intravenously injection (tail vein), s.c. subcutaneous injection, PFU, plaque forming unit.(B and C)Body weight (B) and Tumor growth (C) of tumor-bearing mice. Data are shown in means ± SDs. N.S. Not significant. *P < 0.05, compared with the combination group. (D) At experimental endpoints, mice were anesthetized and sacrificed. Tumors weresubsequently dissected and photographed. (E)Intratumoral expression of Ki-67 and Cleaved-Caspase-3. (F) Immunohistochemistry was performed to analyze the expression of Ki-67 and Cleaved-Caspase-3. Relative protein expressions were quantified with Image-Pro Plus 6.0 (IPP 6.0) N.S., not significant. *P < 0.05.