Abstract
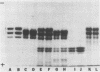
The major globulin of the French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) undergoes a reversible pH-dependent polymerization. At pH values above 6.5, the monomeric form of the protein predominates; and at pH values below 6.5, the protein occurs as a polymer, probably a tetramer. At extremes of pH, the protein dissociates further into peptides. The reversible pH-dependent interaction between globulin subunits is used in this report as the basis for an affinity chromatography procedure for isolation of the globulin. The major globulin from several genetic variants can be obtained in gram quantities and does not indicate the presence of any impurities on discontinuous sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernardin J. E., Kasarda D. D., Mecham D. K. Preparation and characterization of alpha-gliadin. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 10;242(3):445–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catsimpoolas N., Campbell T. G., Meyer E. W. Association-dissociation phenomena in glycinin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 May;131(2):577–586. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90432-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. W., Mawer H. M. Studies on protein subunits. II. Preparation and properties of active subunits of aldolase bound to a matrix. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Mar;149(1):136–145. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON P., SHOOTER E. M. The globulins of the ground nut. (Arachis hypogaea) I. Investigation of arachin as a dissociation system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Jun;5(3/4):361–375. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowland J. Protein synthesis directed by the RNA from a plant virus in a normal animal cell. Genetics. 1974 Sep;78(1):383–394. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.1.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero J., Sun S. M., McLeester R. C., Bliss F. A., Hall T. C. Heritable Variation in a Polypeptide Subunit of the Major Storage Protein of the Bean, Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 1975 Dec;56(6):776–779. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.6.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. M., Hall T. C. Solubility characteristics of globulins from Phaseolus seeds in regard to their isolation and characterization. J Agric Food Chem. 1975 Mar-Apr;23(2):184–189. doi: 10.1021/jf60198a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. M., McLeester R. C., Bliss F. A., Hall T. C. Reversible and irreversible dissociation of globulins from Phaseolus vulgaris seed. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2118–2121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]