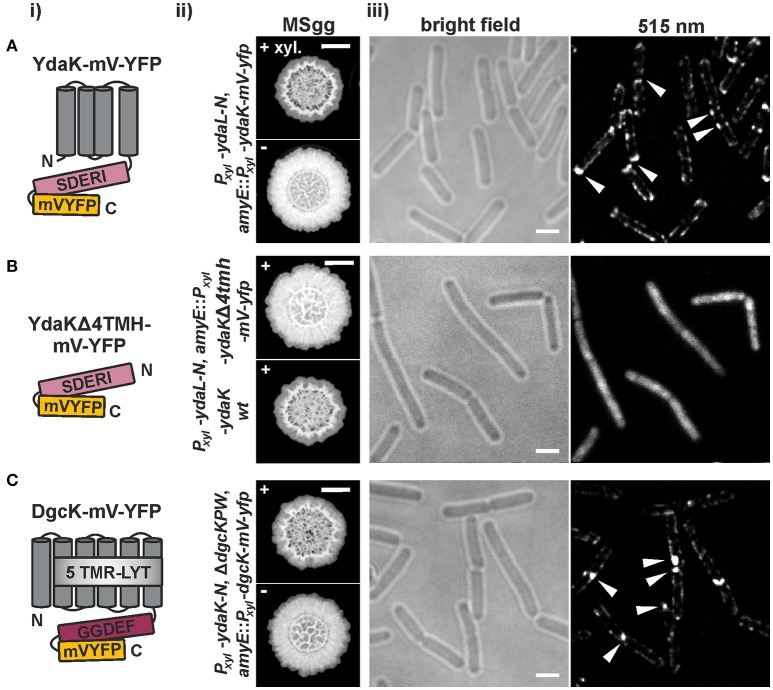
Figure 3.
Functional translational mV-YFP-fusions of the c-di-GMP receptor YdaK and of the synthase DgcK form subcellular assemblies at the cell poles and septa of exponentially growing B. subtilis NCIB3610 (i) Schematic representation of (A) YdaK-mV-YFP-, (B) YdaKΔ4TMH-mV-YFP- and of (C) DgcK-mV-YFP- domain organization and topology (predicted by SMART). Gray, TM helices; light gray, predicted TM-receptor domain 5TMR–LYT; purple, GGDEF domain; light purple, GGDEF domain harboring the degenerated active site motif SDERI; yellow, C-terminal mV-YFP. (ii) Verification of functionality of (A) YdaK-mV-YFP (strain: NCIB3610-PB56-PB57; Pxyl-ydaL-N, amyE::Pxyl-ydaK-mV-yfp) and of (C) DgcK-mV-YFP (strain: DS1809-PB55-PB90; ΔdgcK, -P, -W, Pxyl-ydaK-N, amyE::Pxyl-dgcK-mV-yfp). (B) Colony morphology of strain NCIB3610-PB56-PB100 (upper panel, Pxyl-ydaL-N, amyE::Pxyl-ydaKΔ4tmh-mV-yfp) and NCIB3610-PB56-PB16 (lower panel, Pxyl-ydaL-N, amyE::Pxyl-ydaK) in the presence of 0.1% (v/v) xylose. Altered colony morphology in the presence of xylose reflects EPS production by the products of the yda operon and functionality of the corresponding fusion proteins. Unaltered colony morphology of strain NCIB3610-PB56-PB100 in contrast to strain NCIB3610-PB56-PB16 (lower panel, Pxyl-ydaL-N, amyE::Pxyl-ydaK) reflects inability of YdaKΔ4TMH-mV-YFP to stimulate EPS production. Scale bars: 5 mm. (iii) Mid-exponential-phase B. subtilis NCIB3610 cells expressing (A) ydaK-mV-yfp (strain: NCIB3610-PB56-PB57; Pxyl-ydaL-N, amyE::Pxyl-ydaK-mV-yfp), (B) ydaKΔ4tmh-mV-yfp (strain NCIB3610-PB56-PB100; Pxyl-ydaL-N, amyE::Pxyl-ydaKΔ4tmh-mV-yfp) and (C) dgcK-mV-yfp (strain NCIB3610-PB90, amyE::Pxyl-dgcK-mV-yfp) from the amylase locus, 45 min after induction with 0.1% xylose. Bars: 2 μm. White triangles indicate subcellular clustering of YdaK-mV-YFP and DgcK-mV-YFP respectively.