Figure 2.
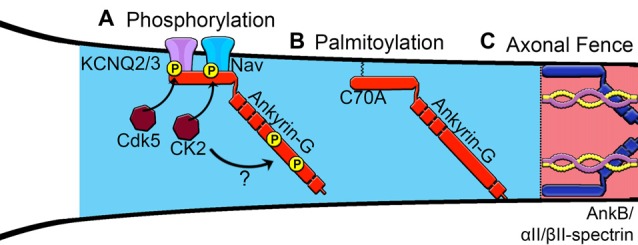
Proposed mechanisms of assembly of the AIS. (A) Phosphorylation of Nav channels by protein kinase casein kinase II (CK2) and KCNQ2/3 channels increases affinity for ankyrin-G. Phosphorylation sites within the giant exon of ankyrin-G (red), potentially regulated by CK2, are important for βIV-spectrin binding. (B) Palmitoylation of a critical cysteine 70 residue in the membrane-binding domain of ankyrin-G is necessary to target ankyrin-G to the AIS and recruit known binding partners. (C) Ankyrin-B interacts with αII-spectrin and βII-spectrin to establish an intracellular barrier or “axonal fence” and maintain ankyrin-G within the proximal axon.
