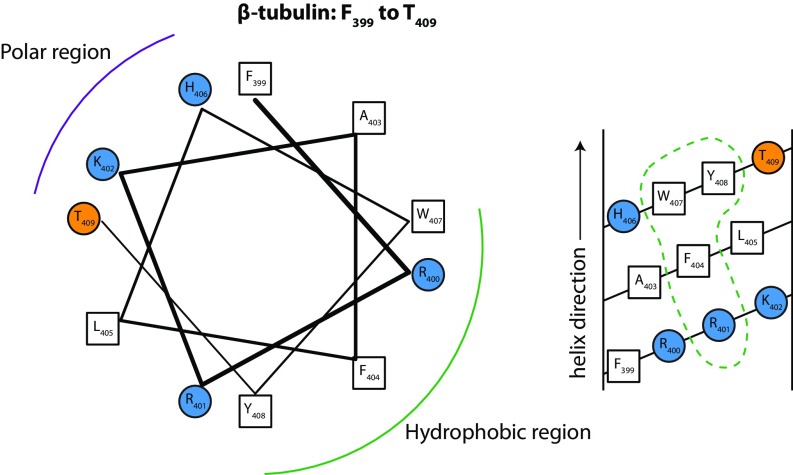
Fig. S7.
Helical wheel (Left) and helical net (Right) diagrams for a possible β-tubulin binding surface identified by NR (Fig. 6D). This surface comprises several distinct regions, including helix H2, which is quite polar; a polar loop from 94 to 101; a group of four hydrophobic valine residues between 171–182; helix H6, which has quite a lot of hydrophobic character, but in the 1TVK structure is not clearly facing the membrane; and helix H11, which like α-tubulin has a hydrophobic patch with conserved tryptophan W407 (see Table S3 and helical wheel and net diagrams here). Of these, only helix H11 is net cationic. Fig. S3 shows that in all-atom MD simulations all contacts between W407 and lipids are short-lived and β-tubulin drifts away from the bilayer surface. Helix H11 forms only transient interactions with lipids as well (Fig. S4).