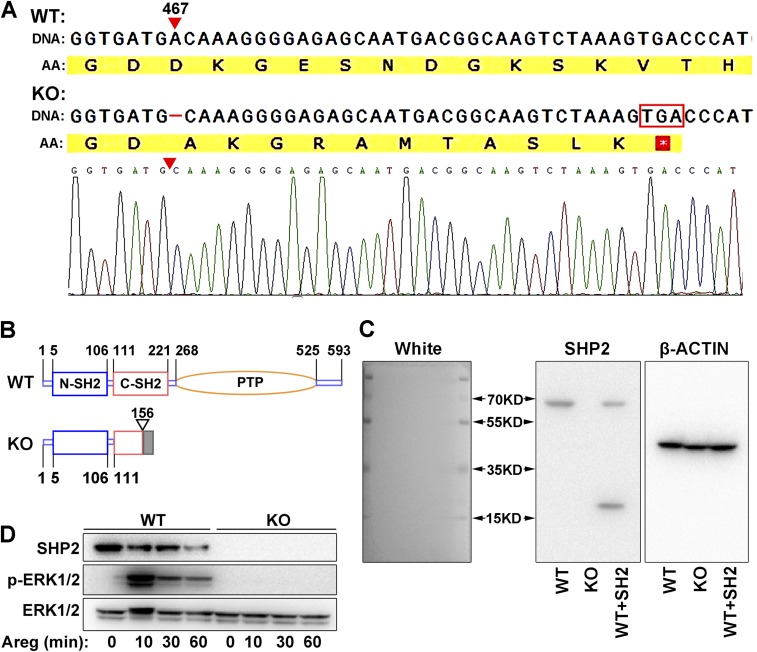
Fig. S4.
SHP2 knockout human endometrial Ishikawa cell line was established by CRISPR/Cas9 strategy. (A) Sanger sequence of SHP2 gene in the knockout cells. A base of nucleic acid was deleted at 467 of coding sequence resulting in frameshift mutation and the translation termination by a stop codon soon after the mutant site. AA, amino acid sequence. (B) Schematic diagram of the structure of wild-type (WT) SHP2 and its mutant form (KO) by CRISPR/Cas9 strategy. (C) Immunoblotting analysis SHP2 protein in WT and KO Ishikawa cells by specific antibody (BD Transduction Laboratories, 610621) that identifies the N-terminal of SHP2. WT cell line transfected with ΔPTP mutant containing only the SH2 domains serves as positive control (WT+SH2). β-Actin is used as loading control. (D) Induction of ERK1/2 phosphorylation in response to amphiregulin (Areg) treatment in WT and KO cells. ERK and its phosphorylation status were analyzed by immunoblotting, showing the functional loss of SHP2 in KO cells.