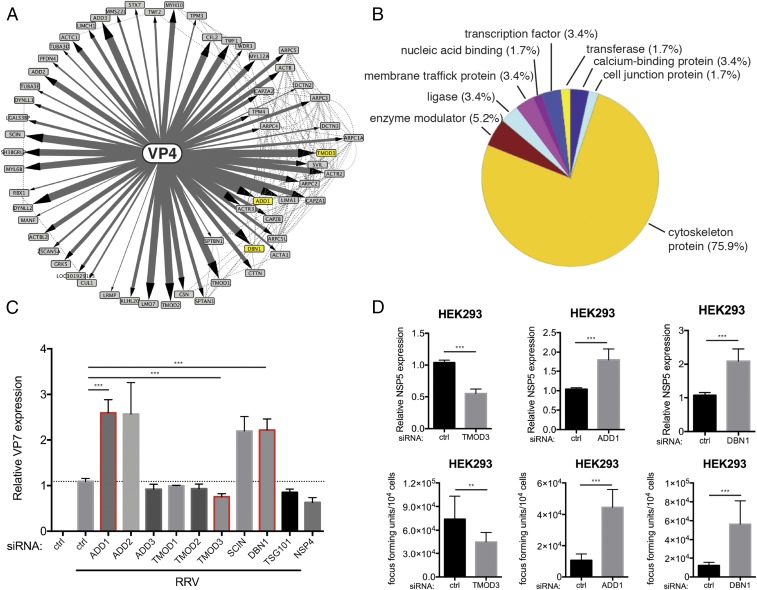
Fig. 1.
VP4 proteomic network reveals cytoskeleton-binding proteins that modulate RV infection. (A) Interactome of the bait viral protein (VP4) and high-confidence host binding proteins. Solid lines with arrowheads represent interactions identified in this study. The width of lines corresponds to the strength of interaction detected in the IP–MS experiment. Dotted lines represent publicly curated protein–protein interactions. The proteins studied in this paper are highlighted by yellow nodes. (B) Pie chart of PANTHER functional classification of VP4-interacting proteins shown in A. (C) HEK293 cells were transfected with indicated siRNA for 48 h and infected with simian RV RRV strain at MOI = 1 for 24 h. Levels of RV replication were measured by RT-qPCR examining the expression of viral gene VP7, normalized to that of GAPDH. The genes studied in this paper are outlined by red boxes. (D) Same experiment as in C except that viral gene NSP5 was measured instead of VP7 by RT-qPCR and virus titer in the supernatants was determined by a focus-forming unit (FFU) assay. For C and D, experiments were repeated at least five times. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance is determined by Student’s t test (**P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001).