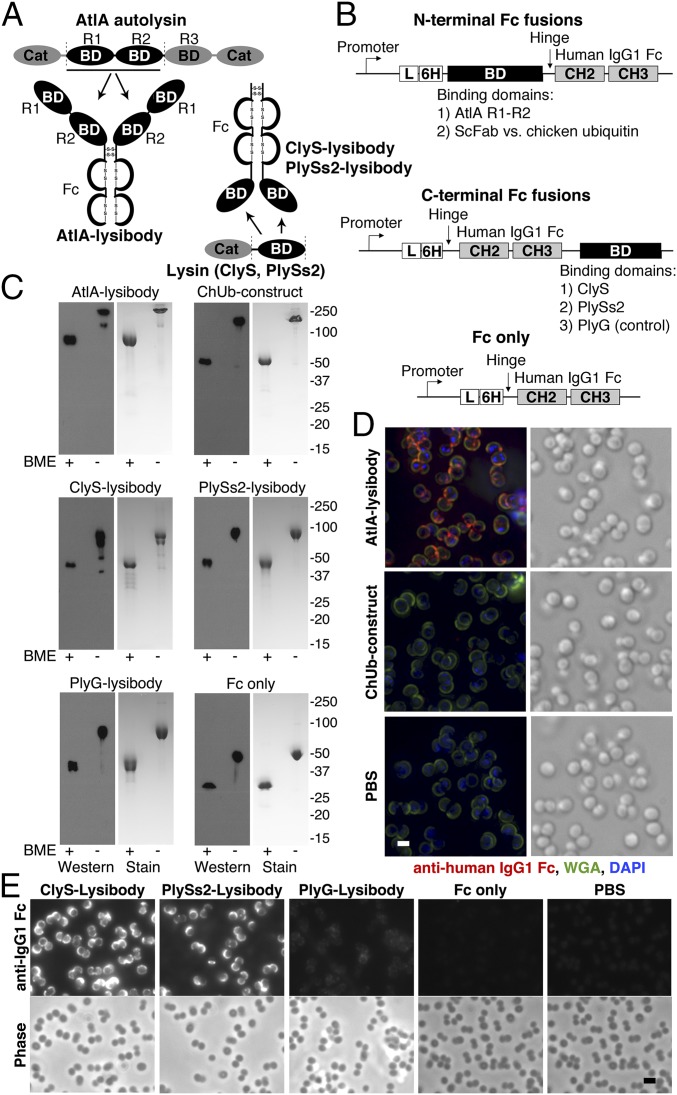
Fig. 1.
Lysibody construction, dimerization, formation of disulfide bridges, and binding to target organisms. (A) Schematic representations of lysibody structure. BD, binding domain; Cat, catalytic domain. (B) Structure of the expression vectors for lysibodies and controls. L, leader sequence; 6H, hexahistidine tag. (C) Purified lysibodies were run on 10% SDS/PAGE with or without the reducing agent BME and analyzed by Western blot using anti-human IgG1 Fc antibody. A duplicate gel was stained with Coomassie blue. (D) Binding of AtlA lysibody to S. aureus Wood 46 (protein A negative) was determined by deconvolution immunofluorescence microscopy. Maximum intensity projections are presented. Anti-human IgG Fc Alexa Fluor 594 conjugate, red; wheat germ agglutinin (WGA), green; DAPI, blue (scale bar, 1 μm). (E) Binding of C-terminal Fc fusion lysibodies to S. aureus Wood 46 was determined by immunofluorescence microscopy, using anti-human IgG Fc Alexa Fluor 594 conjugate (scale bar, 2 μm). Experiments were repeated three times. ScFab, single chain fragment antigen-binding.