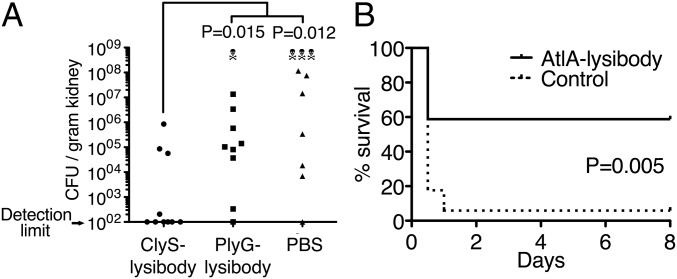
Fig. 5.
Lysibodies protect mice from MRSA infection in kidney abscess and bacteremia models. (A) Five-week-old female BALB/C mice were injected i.p. with 1 mg of the S. aureus-specific ClyS lysibody, B. anthracis-specific PlyG lysibody, or PBS. One day later, the mice were injected i.p. with 2.5 × 106 S. aureus USA600 (methicillin-resistant, vancomycin-intermediate) in 5% mucin. Mouse viability was monitored daily for 4 d, at which time the mice were euthanized, and the bacterial load per gram in the kidneys was determined through homogenization, serial dilution, and plating. Aggregate data from four experiments are presented (n = 10 in each group). Statistical significance was determined using two-tailed Mann–Whitney test. (B) Five-week-old female BALB/C mice were injected i.p. with 0.3 mg AtlA lysibody or PBS (n = 17 in each group). One day later, mice were injected i.p. with 2 × 106 S. aureus MW2 (USA400, methicillin-resistant) in 5% mucin. Mouse viability was monitored for 8 d. Data represent aggregate results from four experiments. Statistical significance was determined using the Gehan–Breslow–Wilcoxon test.