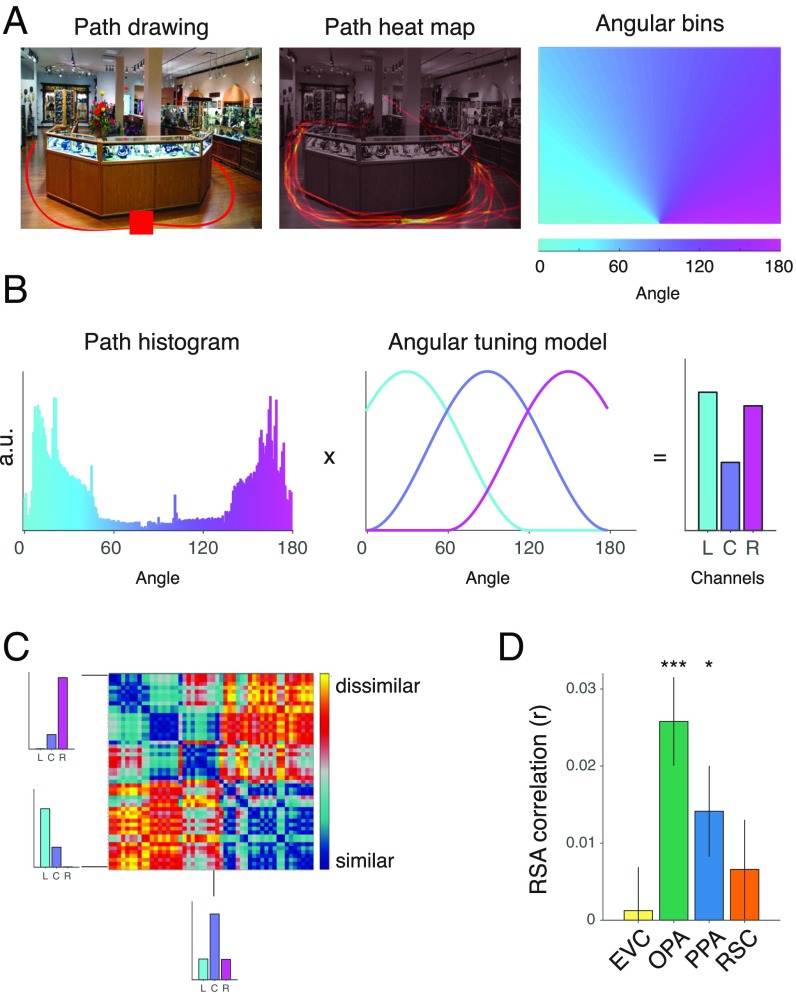
Fig. 3.
Coding of navigational affordances in natural scenes. (A) In a norming study, a group of independent raters were asked to indicate the paths that they would take to walk through each scene starting from the bottom center of the image (Left). These data were combined across raters to produce a heat map of the possible navigational trajectories through each scene (Center). Angular histograms were created by summing the responses within a set of angular bins radiating from the bottom center of each image (Right). (B) The resulting histograms summarize the trajectory responses across the entire range of angles that are visible in the image. Navigational affordances were modeled using a set of hypothesized encoding channels with tuning curves that broadly code for trajectories to the left (L), center (C), and right (R). Model representations were computed as the product of the angular-histogram vectors and the tuning curves of the navigational-affordance channels. a.u., arbitrary units. (C) A model RDM was created by comparing the affordance-channel representations across images. (D) RSA showed that the strongest effect for the coding of navigational affordances was in the OPA. Error bars represent ± 1 SEM; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001.