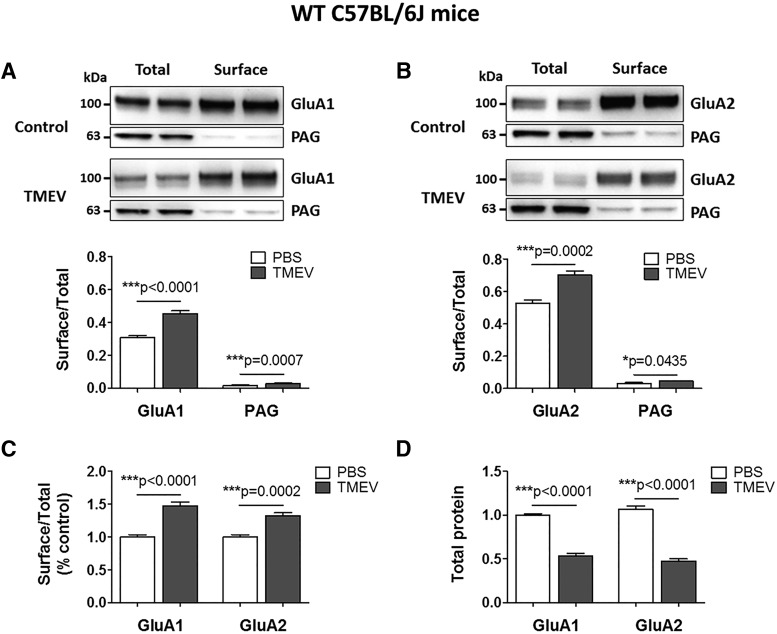
Figure 7.
Increase in the cell-surface levels of GluA1 and GluA2 subunits of AMPARs in TMEV-infected WT C57BL/6J mice during acute seizures. (A) Representative immunoblots from two mice show the levels of GluA1 in the total as well as the cell-surface fractions of proteins isolated from ipsilateral hippocampus at 5 d postinjection of PBS (control) or TMEV. Data in the first (total) and the third (surface) lanes from the left are from the same mouse, and the second (total) and the fourth (surface) lanes correspond to the other mouse. The surface proteins were isolated from the intracellular proteins by cell-surface biotinylation in acute hippocampal slices. Levels of GluA1 were quantified by densitometry, and data are shown as ratio of surface to total protein, which is significantly increased in TMEV-infected mice (n = 6). PAG is a mitochondrial protein and serves as an intracellular control protein. (B) Similar to GluA1, the ratio of surface/total level for GluA2 is also increased in TMEV-infected mice (n = 6). (C) Ratios of surface/total protein expression for GluA1 and GluA2 are increased by 48% and 33%, respectively (data normalized to control). (D) Approximately 50% decrease in the total expressions of GluA1 and GluA2 in TMEV-infected mice compared with control group. Statistics: unpaired two-tailed t test.