Fig. 5.
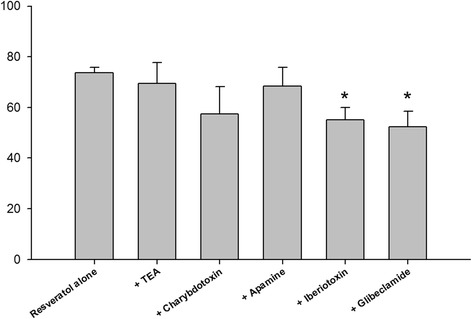
The effects of tetraethylammonium (TEA), charybdotoxin, apamine, iberiotoxin, and glibenclamide on resveratrol-induced relaxation in the human gallbladder. TEA (1 mM), apamine (100 nM), and charybdotoxin (100 nM) had no significant effect on resveratrol-induced relaxation of human gallbladder muscle strips (p > 0.05, n ≥ 4). In contrast, iberiotoxin (200 nM) and glibenclamide (10 μM) significantly inhibited resveratrol-induced relaxation of human gallbladder muscle strips (p < 0.05, n = 7). The vertical bars represent ± standard error of the mean (SEM)
