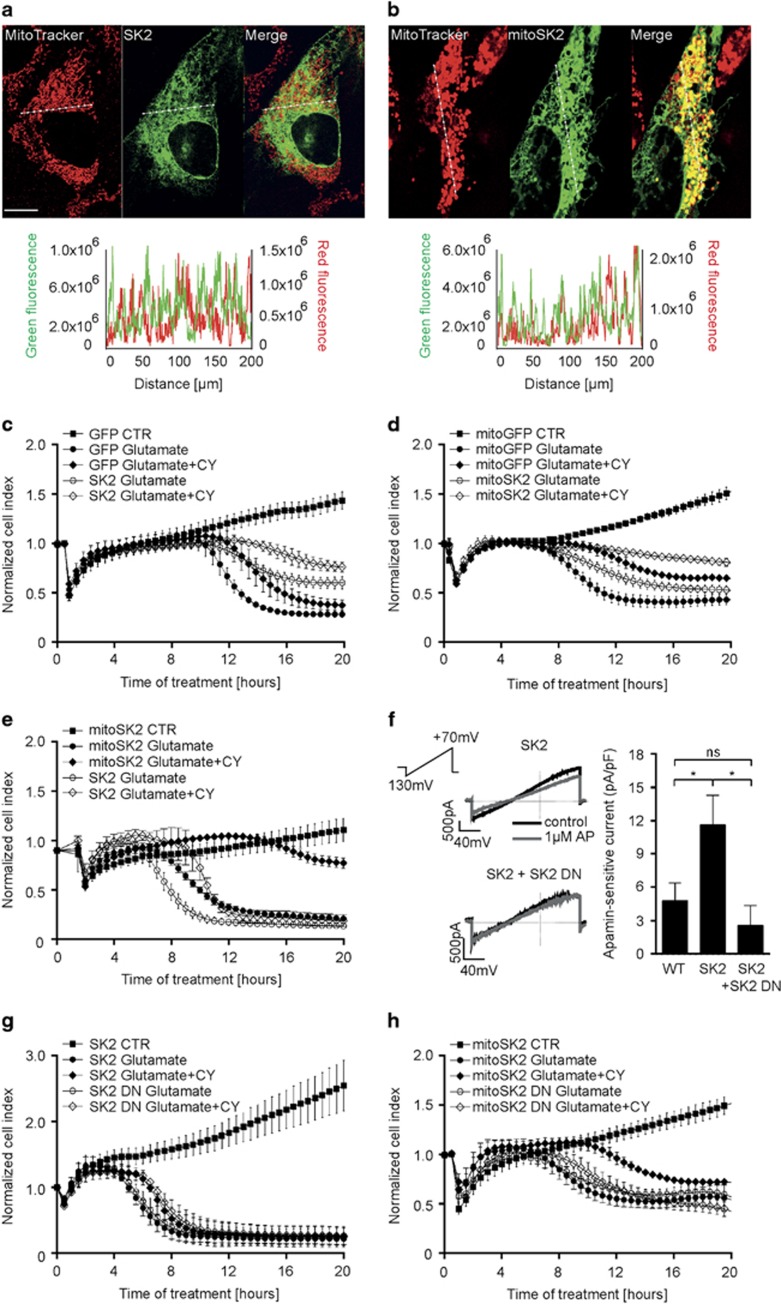
Figure 1.
Overexpression of mitochondrial SK2 channels enhances CyPPA-mediated protection against glutamate-induced cell death. (a, and b) Representative confocal images of HT22 cells overexpressing (a) non-targeted GFP-tagged SK2 channel or (b) mitochondrial SK2 channel co-localizing with mitochondria (MitoTracker Red) (n=10–15 cells/plasmid). Lower panels: plot profile of GFP and MitoTracker Red along the dashed line. Scale bars: 10 μm. (c–e) xCELLigence measurement of cell viability during glutamate exposure in the presence or absence of CyPPA (CY) in cells overexpressing (c) GFP control and SK2, (d) mitoGFP control and mitoSK2, or (e) SK2 and mitoSK2 (mean±SD, n=6–8). (f) Electrophysiological recordings of apamin-sensitive currents in HT22 cells transfected with the SK2 alone or SK2 combined with SK2 DN before and after application of 1 μM apamin (AP). Left panel: representative whole-cell currents. Right panel: quantification of apamin-sensitive currents. Data are shown as mean±SEM, n=6, paired Student's t-test, *P<0.05, ns not significant. (g and h) xCELLigence measurement of cell viability during glutamate exposure in the presence or absence of CyPPA (CY) in cells overexpressing (g) SK2 and SK2 DN, or (h) mitoSK2 and mitoSK2 DN (mean±SD, n=6–8)