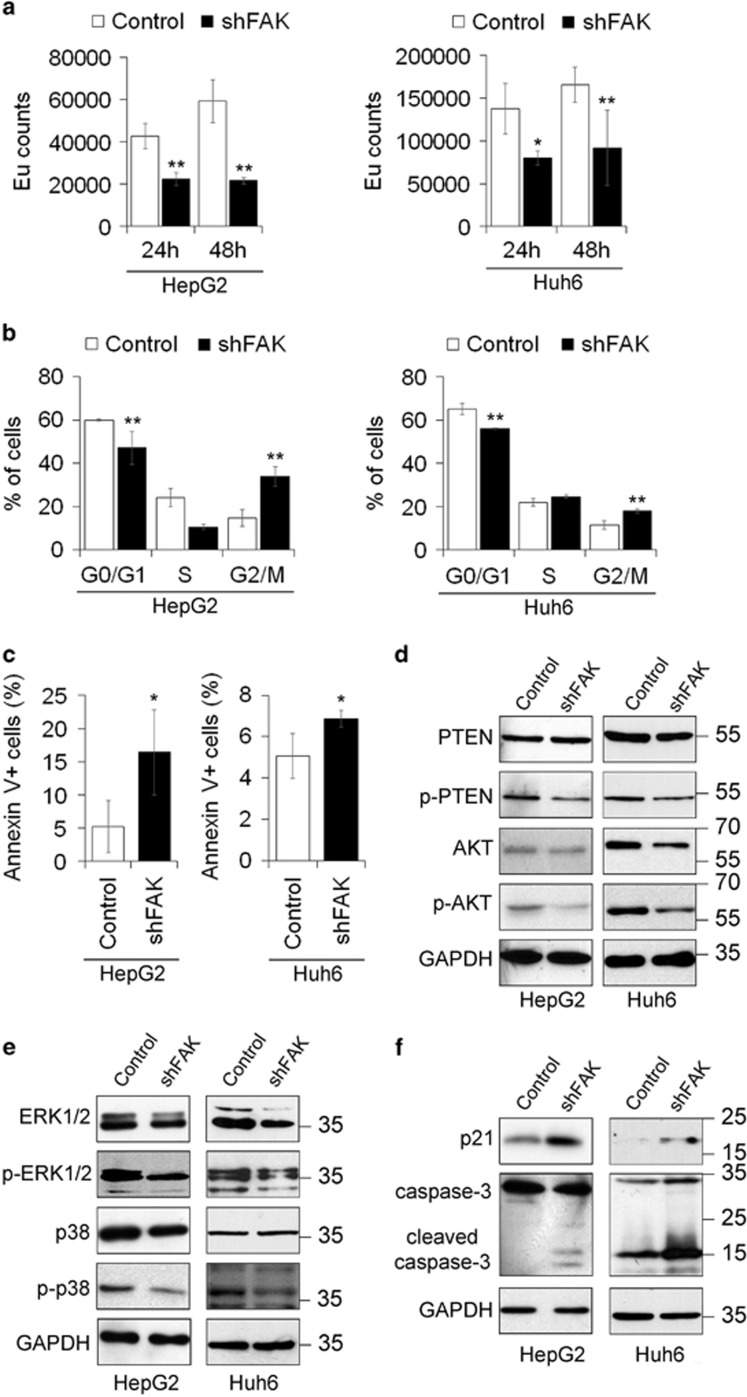
Figure 1.
FAK depletion inhibits growth and promotes apoptosis in HCC cells. (a) Cell proliferation assayed via a BrdU incorporation kit and expressed as Europium (Eu) counts in Control and shFAK HepG2 and Huh6 cells. Values are mean±SD (*P< 0.05;**P<0.01; n=4). (b) Distribution of Control and shFAK HepG2 and Huh6 cells in G0/G1, S and G2/M phase of the cell cycle by propidium iodide (PI) staining and flow cytometric analysis. Values are plotted as mean±SD (**P<0.01; n=3). (c) Percentage of apoptotic Control and shFAK HepG2 and Huh6 cells measured by Annexin V and flow cytometry. Values are plotted as mean±SD (*P<0.05; n=3). (d) Representative western blots (WB) for PTEN and p-PTEN, and for AKT and p-AKT in Control and shFAK HepG2 and Huh6 cells. (e) Representative WB for ERK1/2 and p-ERK1/2, and for p38 and p-p38 in Control and shFAK HepG2 (n=3) and Huh6 cells (n=2). (f) Representative WB for p21 and caspase-3 in Control and shFAK HepG2 (n = 2) and Huh6 cells (n = 2). GAPDH is reported as a loading control