Figure 7.
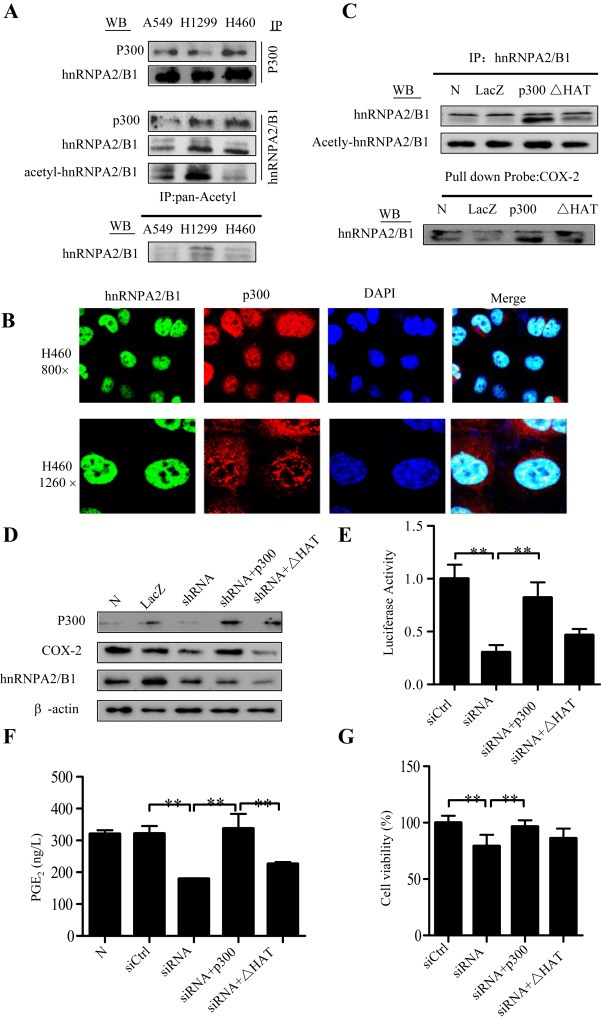
Acetylation of hnRNPA2/B1 by p300. (A) Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) assays with anti‐p300, anti‐hnRNPA2/B1, or anti‐pan‐Acetyl antibody. Western blot (WB) assays were performed the antibodies against anti‐hnRNPA2/B1 and anti‐p300. (B) Cellular co‐localization of p300 and hnRNPA2/B1 in H460 cells was detected by confocal immunofluorescence assay. (C) H1299 cells were transfected with the expressing plasmids of p300 or its HAT deletion mutant. LacZ was used for the control. After 48 h, the nuclear extracts were used for IP assay using anti‐hnRNPA2/B1 antibody following by WB assay using anti‐hnRNPA2/B1 or anti‐pan‐Acetyl antibody, and for DNA‐binding protein pulldown assay using biotin‐labeled COX‐2 promoter probe following by Western blot assay using anti‐hnRNPA2/B1. (D–G) H460 cells were transfected with hnRNPA2/B1 shRNA combining with the expressing plasmids of p300 or its HAT deletion mutant. After 48 h, the effects of the shRNA on COX‐2 protein (D), COX‐2 promoter (−459/+9) activity (E), PGE2 production in cell culture media (F), and cell viability (G) were determined, respectively. The data is the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. p < 0.05 represents significant difference.
