Figure 7.
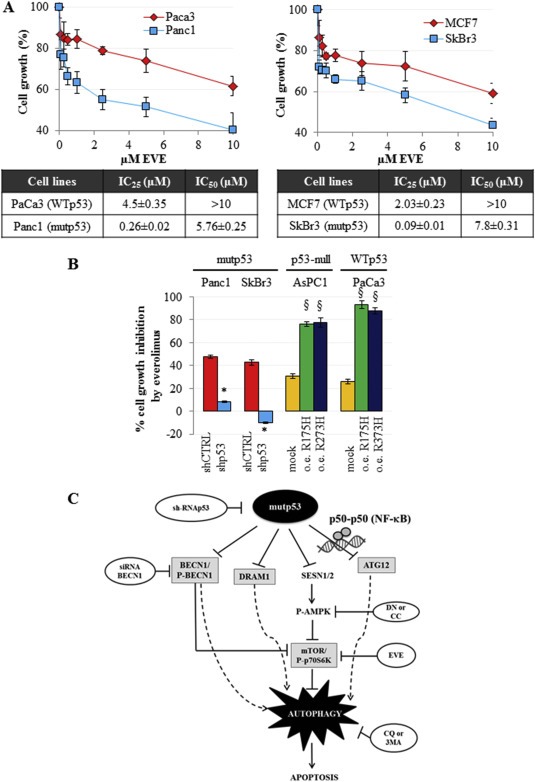
Mutant p53 sensitizes cancer cells to everolimus. (A) Cells were seeded in 96‐well plates and treated for 48 h with increasing concentrations of everolimus. Cell growth was measured using the crystal violet colorimetric assay and IC25 and IC50 values for each cell line tested have been reported. (B) Cells were seeded in 96‐well plates and transfected with pRSuper‐p53 vector (shp53) and with the plasmids coding for mutant p53 proteins (R175H or R273H), or with empty pRSuper (shCTRL) or pCDNA3 (mock), respectively, as negative controls. For each experimental condition, cells were untreated or treated with 5 μM everolimus for 48 h. Cell growth was determined using the crystal violet colorimetric assay. The rate of cell growth inhibition corresponds to the effect of everolimus, as compared to vehicle (untreated), in each indicated transfection condition. These experiments were at least biological triplicates. The P‐values were calculated with two‐tailed t‐test. Statistical analysis: *p < 0.05 shp53 vs shCTRL; §p < 0.05 R175H or R273H vs mock. (C) Model of the molecular mechanism unraveled in the present study.
