Figure 1.
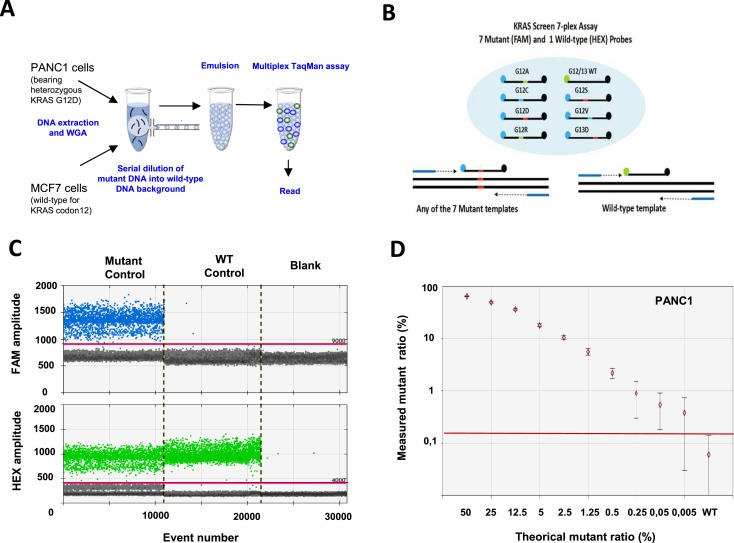
Sensitivity of the KRAS multiplex assay by droplet digital PCR. A. Protocol. DNA was extracted from 100 PANC1 cells bearing a heterozygous mutation c.35G > A in KRAS codon 12 (Gly12Asp) and 100 MCF7 cell lines (wild‐type for KRAS codon 12–13). After whole genome amplification, DNA from the two cell lines was mixed and droplet digital PCR was performed using a multiplex KRAS assay. B. KRAS screening assay. This TaqMan assay is designed to detect the seven most frequent mutations in codon 12 and codon 13 of KRAS. C. Experimental validation. 1D‐Dot plot. The blue histogram indicates the number of droplets considered as positive for mutant KRAS according to the fluorescence threshold. The green histogram corresponds to the number of wild‐type droplets. Mutant control, DNA containing a 1:1 mix of mutant and wildtype KRAS. WT control, DNA containing only KRAS wild‐type. Blank, water. D. Mutant ratio threshold determination (mutant copies/total copies in %) according to theoretical mutant ratio obtained by serial dilution. The red line indicates the detection threshold.
