Figure 1.
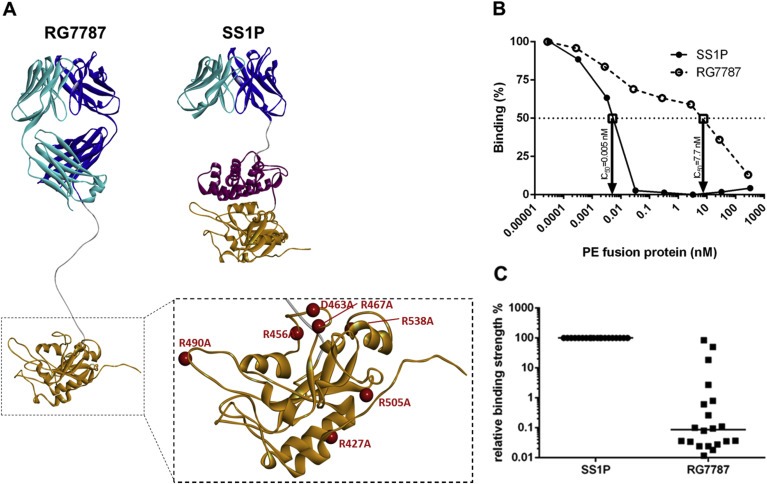
Structures of RG7787 and SS1P and assessment of their relative antigenicity (A) Ribbon diagrams showing the different domain structures of SS1P and RG7787 as well as the 7 amino acid substitutions (red balls) within the catalytic domain III of PE that were introduced in RG7787 to silence all 6 known human B‐cell epitopes. The mutated PE24 was modeled onto the crystal structure of PE (structure 1IKQ in the Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics protein data base), the linker with the furin cleavage site was modeled as linear peptide chain and energy minimized, and the Fab fragment was modeled onto fragments of different Fv structures and refined as described in Bujotzek et al., 2015. (B) The graph shows typical competition curves obtained using serum from an SS1P‐treated patient with a neutralizing anti‐drug antibody response. In this case the concentrations of RG7787 and SS1P at which binding to PE38 was inhibited by 50% (IC50) were 7.7 nM and 0.005 nM, respectively. Based on these IC50 values the binding ratio of SS1P/RG7787 was 0.065%. (C) Binding ratios for sera from 20 patients were plotted and the median binding ratio is indicated by a horizontal line.
