Figure 2.
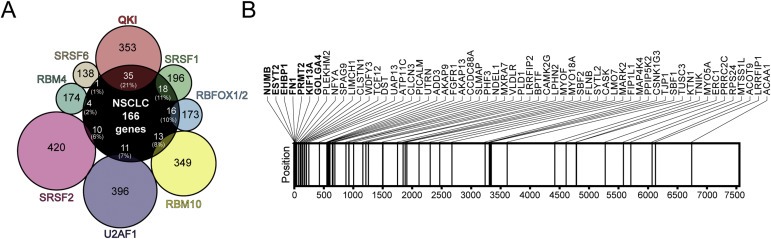
QKI is a key regulator of splicing in NSCLC. A. Venn diagram of the targets of lung cancer‐related splicing factors common to 166 genes corresponding to top 250 differentially‐spiced events identified by ExonPointer. The list of targets was obtained from the literature: QKI (Zong et al., 2014), SRSF1 (de Miguel et al., 2014), RBFOX1/2 (Zhang et al., 2008), RBM10 (Wang et al., 2013b), U2AF1 (Shirai et al., 2015), SRSF2 (Zhang et al., 2015), RBM4 (Wang et al., 2014) and SRSF6 (Jensen et al., 2014). Approximate percentages represent the proportion of genes in the ExonPointer list that are targets for a given splicing factor. B. Schematic representation of the positions occupied by 60 QKI targets, according to Zong et al. (Zong et al., 2014), in the ranked list generated by ExonPointer. Genes among the top 20 are depicted in bold. Horizontal lines represent the position of each gene in the list. A statistically significant overrepresentation of QKI target genes was observed in the ExonPointer list (P < 0.001).
