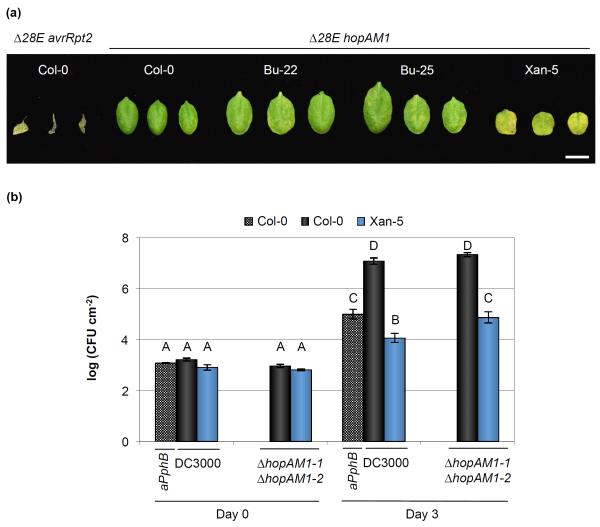
Fig. 6.
HopAM1 recognition influences resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Pst) DC3000 in the Xan-5 Arabidopsis accession. (a) Cell death symptoms 4 d after inoculation with 2 × 107 colony-forming units (CFU) ml−1 of Pst Δ28E carrying pBBR:hopAM1-1 (Δ28E hopAM1) and pUCP19::avrRpt2 (Δ28 avrRpt2). Image was composed from accessions’ individual images from a single experiment. Bar, 1 cm. Pst Δ28E avrRpt2 strain was used to confirm that the strain with 28 effectors deleted was still capable of mounting a hypersensitive response (HR) response in Col-0. (b) HopAM1 recognition is partially responsible for the Pst DC3000 resistance in the Xan-5 accession. Leaves were infiltrated with Pst DC3000, Pst DC3001 ΔhopAM1-1 (ΔhopAM1-1ΔhopAM1-2), and Pst DC3000 pDSK600::avrPphB (aPphB) at an inoculum of 106 CFU ml−1. Error bars show ± SE of 3 and 6 biological samples for day 0 and day 3, respectively. Letters above each bar indicate similar groups as determined with a Tukey HSD test (P < 0.05). A slight reproducible increase in in planta bacterial growth was observed for Xan-5 when inoculated with a strain lacking hopAM1.