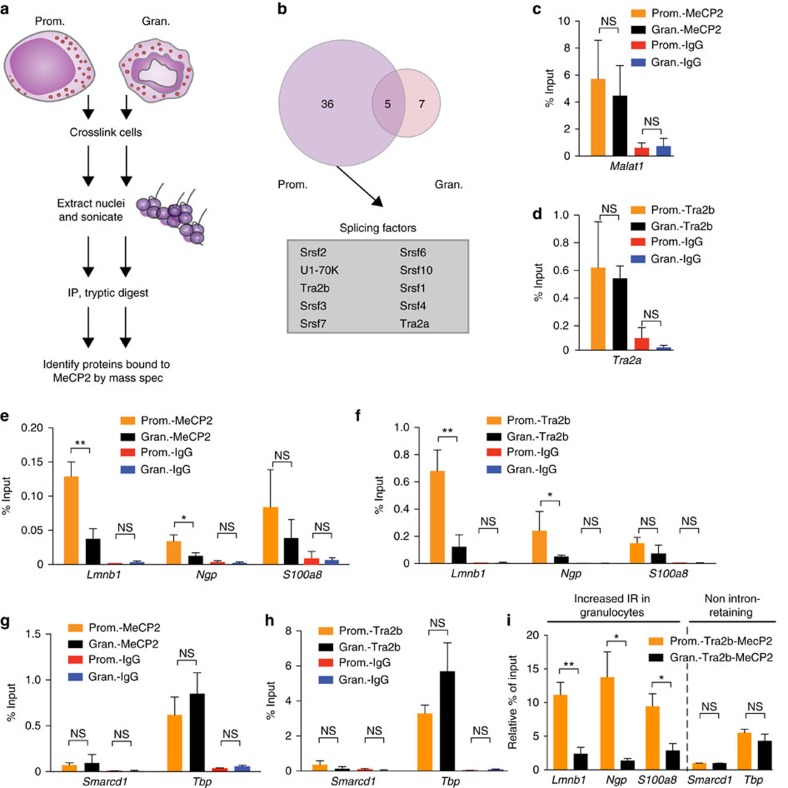
Figure 5. Reduced MeCP2-mediated recruitment of the splicing factor Tra2b promotes IR.
(a) Schematic of the RIME assay to identify MeCP2 binding partners in normal promyelocytes (Prom.) and granulocytes (Gran.). (b) Venn diagram showing proteins that bind to MeCP2 in promyelocytes and/or granulocytes. MeCP2 bound splicing factors enriched in promyelocytes are listed. (c) Occupancies of MeCP2 and (d) Tra2b in the coding region of Malat1 and Tra2a in promyelocytes and granulocytes measured by RNA-IP followed by qRT-PCR. (e) Occupancies of MeCP2 and (f) Tra2b near splice junctions of Lmnb1 intron 5, Ngp intron 3 and S100a8 intron 2 in normal promyelocytes compared to granulocytes by RNA-IP. (g) Occupancies of MeCP2 and (h) Tra2b near splice junctions of constitutively spliced Smarcd1 intron 9 and TBP intron 5 in normal promyelocytes compared to granulocytes by RNA-IP. (i) Occupancies of MeCP2 and Tra2b near splice junctions of Lmnb1 intron 5, Ngp intron 3 and S100a8 intron 2, Smarcd1 intron 9 and TBP intron 5 in normal promyelocytes compared to granulocytes by RNA-IP-reIP. Levels of occupancies are shown relative to background inferred by sequential Tra2b-IgG RNA-IP controls. A two-tailed t-test was used to determine significance, denoted by *P<0.05, **P<0.001 and NS, not significant. Dots and bars display mean±s.e.m. Independent qRT-PCR experiments were performed three to five times in triplicate.