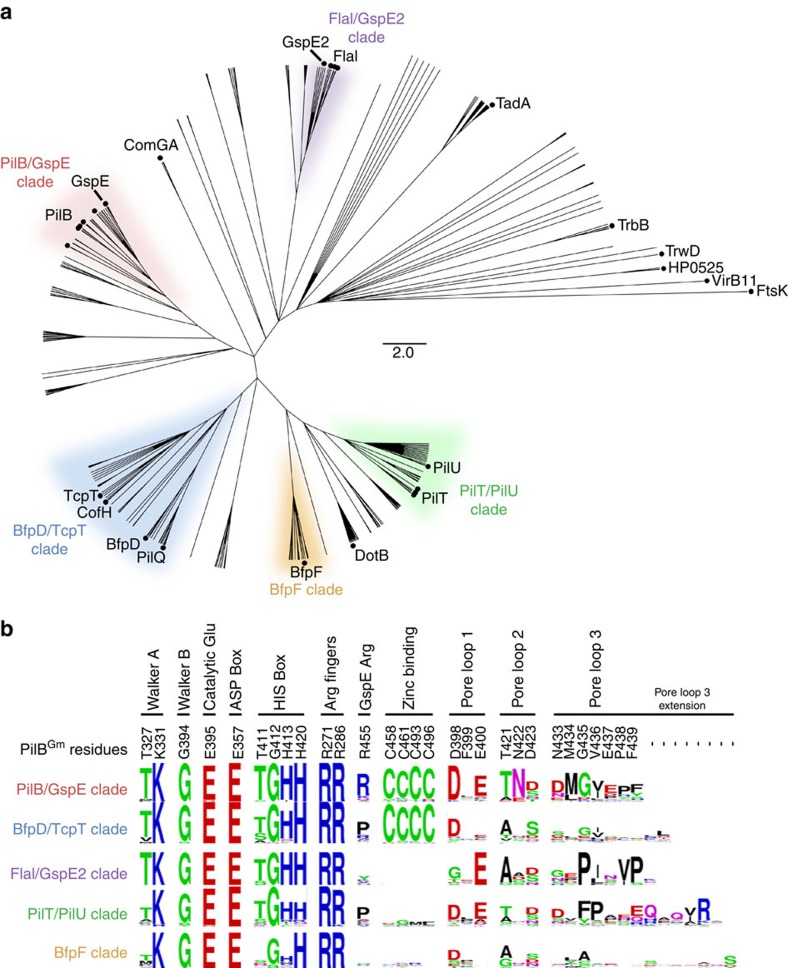
Figure 1. Identification and functional prediction of conserved residues in PilB.
(a) Overview of the phylogenetic analysis of PilT-like ATPase family members. Sequences from model systems are identified with a black circle and labelled. There are multiple circles for PilB, PilT and FlaI reflecting that there are multiple model systems from different species for these proteins. For a detailed view of the phylogenetic tree including the identity of branches not labelled here see Supplementary Fig. 1. Only branches with a >85% bootstrap value are shown (1,000 bootstraps). FtsK was used as an out-group. Protein sub-families, labelled as clades, are given a unique colour for clarity and to stratify the sequences for further analysis. (b) Sequence logo representation of conserved residues stratified based on the clade definitions above. Each dash indicates that there is no corresponding residue in PilB from G. metallireducens.