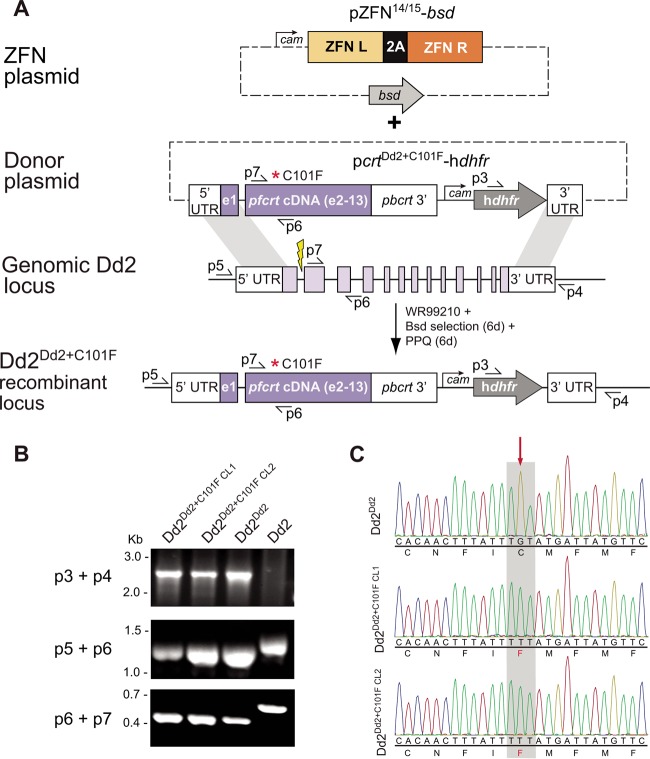
FIG 1 .
Zinc finger nuclease (ZFN)-mediated editing strategy of Dd2. (A) Schematic of pfcrt editing, resulting in introduction of the C101F mutation. Dd2 parasites were transformed with the donor plasmid pcrtDd2+C101F-hdhfr. This plasmid carries the cDNA version of a modified Dd2 pfcrt allele harboring the PfCRTC101F mutation as well as a human dhfr cassette that mediates resistance to the selection agent WR99210. Episomally enriched Dd2 parasites were then transformed with the ZFN-expressing plasmid pZFN14/15-bsd. These 2A-linked ZFNs target the pfcrt intron 1-exon 2 junction (yellow thunderbolt). Homologous recombination-based repair, triggered by the ZFN-induced double-stranded break, utilized the donor template to generate the recombinant parasites Dd2Dd2+C101F. (B) PCR-based screening of pfcrt-modified and parental Dd2 parasites. Removal of introns from the pfcrt locus of the recombinant Dd2 parasites yielded shorter PCR amplicons compared to parental Dd2. This screen used the primer pairs p3+p4 (Dd2Dd2+C101F and Dd2Dd2, 2.5 kb; Dd2, no product), p5+p6 (Dd2Dd2+C101F and Dd2Dd2, 1.2 kb; Dd2, 1.4 kb), and p6+p7 (Dd2Dd2+C101F and Dd2Dd2, 0.4 kb; Dd2, 0.6 kb). Primer positions are depicted in panel A. (C) Chromatograms of a region of exon 2 obtained from sequencing pfcrt cDNA from Dd2Dd2 and the two pfcrt-modified clones Dd2Dd2+C101F CL1 and Dd2Dd2+C101F CL2. The red arrow depicts the introduction of the C101F mutation at codon 101 in the edited clones.