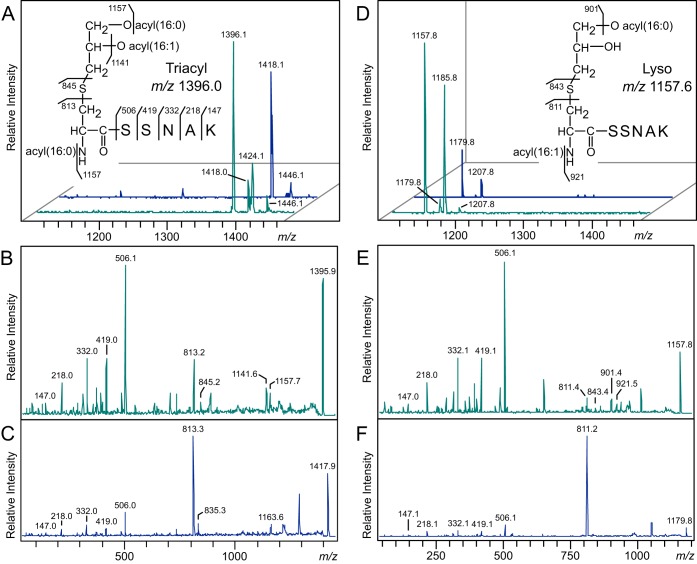
FIG 6.
MALDI-TOF MS of E. coli Lpp(K58A) processed by Lnt and of E. faecalis WMC_RS08810. (A, D) Trypsinized Lpp lipopeptides purified from the wild-type lnt strain KA548 (A) and the lnt null, WMC_RS08810-expressing strain KA532 (D) were eluted from nitrocellulose bands and analyzed by MALDI-TOF MS (turquoise traces). Sodium was added to a subset of samples to promote sodiated adduct formation (blue traces). (B, C) The MS-MS spectra of the protonated m/z 1396 (B) and sodiated m/z 1418 (C) parent ions were used to elucidate the triacylated N-terminal structure of Lpp from KA548 (inset in panel A). (E, F) Likewise, the MS-MS spectra of the ions m/z 1157 (E) and 1179 (F) were used to assign the lyso-form N-terminal peptide structure of Lpp from KA532 (inset in panel D). The positions of the O-acyl chains could not be determined on either the triacyl or lyso-form Lpp molecules.