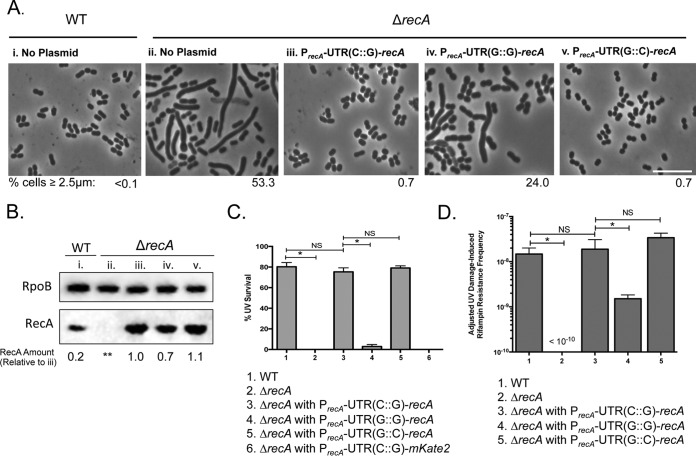
FIG 5.
The recA 5′ UTR governs RecA intracellular concentration. (A) Plasmids used for these experiments were constructed with the recA gene under the control of its native promoter and UTR or with variant UTRs. Plasmids with the native regulatory region [PrecA-UTR(C::G)-recA], the mutated UTR(G::G) [PrecA-UTR(G::G)-recA], or the compensatory UTR(G::C) [PrecA-UTR(G::C)-recA] were introduced by transformation into A. baumannii ΔrecA cells. Untreated cells were imaged, and the percentage of cells equal to or longer than 2.5 μm was measured (shown underneath each representative phase-contrast image). The untreated WT A. baumannii cells have the typical coccobacillary shape of A. baumannii (i) and an undetectable number of elongated cells (<0.1%), while approximately 50% of the cells in the isogenic ΔrecA strain are elongated (ii). The elongation phenotype is rescued to the shorter coccobacilli by the plasmid-borne WT recA gene under the control of its native regulatory region, PrecA-UTR(C::G)-recA (iii), and only partially restored by PrecA-UTR(G::G)-recA (iv). A UTR variant that complements the stem-loop structure, PrecA-UTR(G::C)-recA, also rescued the cell length phenotype (v). Scale bar represents 10 μm. (B) Immunoblot to detect RecA was performed in each strain (lanes i to v) as described for panel A. Equal amounts of cell-free lysates were probed with polyclonal anti-RecA and monoclonal anti-RpoB antibodies (see Materials and Methods). RpoB was measured to account for differences in protein loading between samples. Relative RecA protein from each strain was quantified and standardized to ΔrecA cells with PrecA-UTR(C::G)-recA (lane iii) to compare the effects of altering the UTR structure (values shown below under each lane). RecA levels decrease upon disrupting formation of the UTR structure (lane iv). This value is rescued to native levels by the compensatory mutation in the UTR (lane v). **, undetectable. (C) UV survival (27 J/m2) of WT A. baumannii and isogenic ΔrecA strains with the plasmid-borne recA gene with native and variant 5′ UTRs. Only the strains with the UTRs that maintain a probable stem-loop structure survive UV treatment at WT levels. Error bars represent standard deviations. An unpaired two-tailed t test between indicated strains was used for statistical analysis. *, P < 0.05. (D) DNA damage-induced rifampin resistance acquisition of WT A. baumannii and ΔrecA cells with the plasmid-borne UTR-recA variants. Impairing formation of the major stem-loop results in an ∼10-fold-lower mutation frequency. Error bars represent standard deviations. An unpaired two-tailed t test between indicated strains was used for statistical analysis. *, P < 0.05.