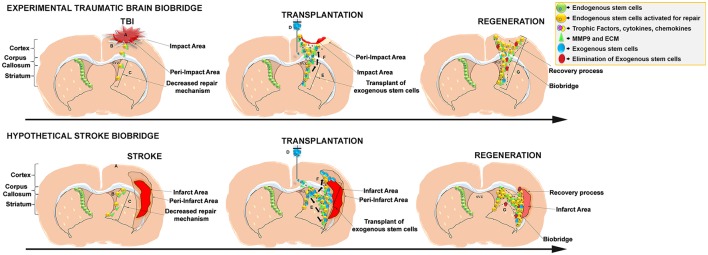
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the stem cell-mediated brain repair in TBI biobridge from our experimental data and hypothetical stroke biobridge. (Top) Transplanted stem cells into the injured TBI brain secrete extracellular matrix and metalloproteinases (MMP-9)forming a biobridge between the neurogenic niche (SVZ) and pre-impact area to guide endogenous stem cells to the area of injury. (A), TBI injury; (B), Activation of endogenous repair mechanisms; (C), Decreased repair Mechanism. (D), Transplant of exogenous stem cells; (E) Exogenous stem cells secretion of trophic factors and MMP9 and ECM able to create biobridges of neurovascular matrix; (F), migration of endogenous cells following the biobridge toward the injury site. (G) Elimination of exogenous cells, but maintenance of recovery processes by endogenous stem cells. (Bottom) Hypothesized formation of the stroke biobridge, thereby transplanted stem cells may also secrete extracellular matrix and metalloproteinases (MMP-9) contributing to the formation of biobridges and enhancing the migration of endogenous stem cells between the neurogenic niche (SVZ) and peri-infarct area of the cortex and peri-infarct area of the striatum. (A), Stroke injury; (B), Activation of endogenous repair mechanisms; (C), Decreased repair Mechanism. (D), Transplant of exogenous stem cells; (E), Exogenous stem cells secretion of trophic factors and MMP9 and ECM able to create biobridges of neurovascular matrix; (F), Migration of endogenous cells following the biobridge toward the cortex, and striatum (site of injury). (G), Elimination of exogenous cells, but maintenance of recovery processes by endogenous stem cells.