Figure 1. Interactions of the Snf5 module in SWI/SNF.
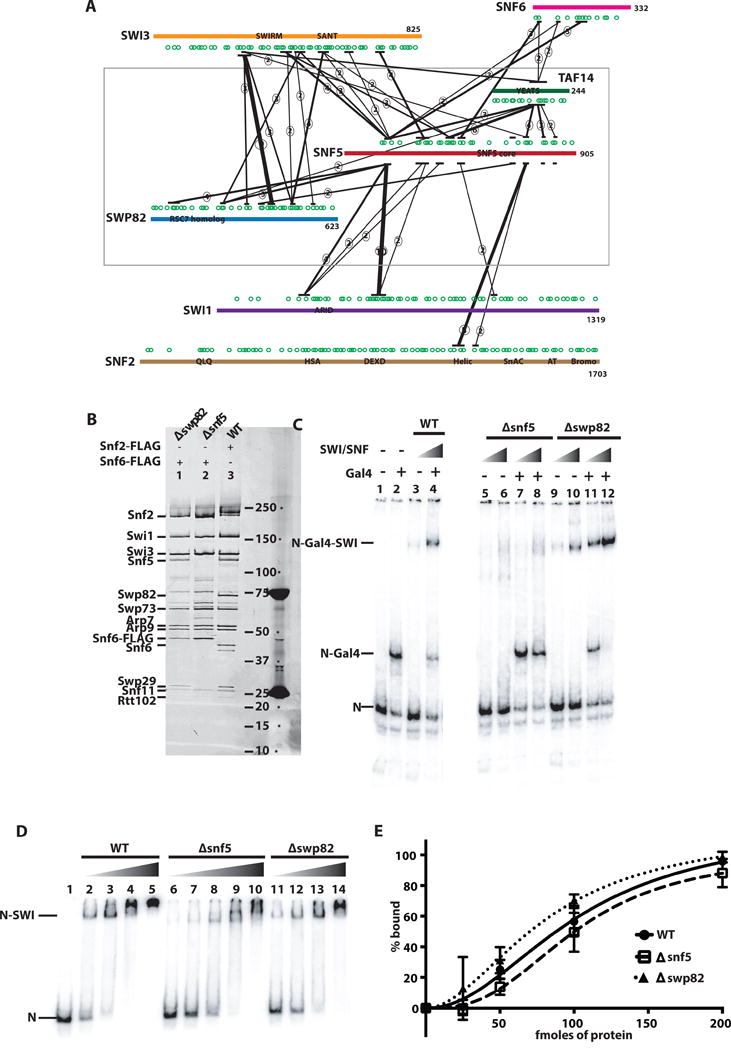
(A) The interactions of Snf5 with other subunits in the SWI/SNF complex were determined by crosslinking with the homo-bifunctional, lysine-specific crosslinker BS3 and subsequent analysis by mass spectrometry. The SWI/SNF subunits shown are Snf2 (brown), Swi1 (purple), Swi3 (orange), Swp82 (blue), Snf6 (magenta) and Taf14 (green). Lysine residues are indicated by green circles and the labeled boxes are the conserved domains. Only those interactions in which 2 or more crosslinks were detected in a region spanning ~30 amino acids are shown and the number of crosslinks detected are indicated by the circled numbers. The thickness of the black line is also indicative of the number of crosslinks detected in that region. (B) SWI/SNF complexes were purified by immuno-affinity chromatography with either Snf5 or Swp82 deleted and analyzed on a 4–20% SDS polyacrylamide gel. Wild type SWI/SNF (lane 3) contains two FLAG tags at the C-terminus of Snf2. Snf6 was tagged with a double FLAG tag at its C terminus in the Δsnf5 (lane 2) and Δswp82 (lane 1) SWI/SNF complexes. (C) Recruitment of wild type and mutant SWI/SNF by the acidic transcription activator Gal4-VP16 was tracked by gel shift analysis. Nucleosomes alone (N), nucleosomes bound by Gal4-VP-16 (N-Gal4) and nucleosomes bound by SWI/SNF with or without Gal4-VP16 (N-Gal4-SWI) migrated at the indicated positions. Gal4-VP16 was added to lanes 2, 4, 7, 8, 11, and 12. Wild type, Δsnf5 and Δswp82 SWI/SNF were add in lanes 3–4, 5–8, and 9–12, respectively. (D) Purified SWI/SNF complexes from wild type (WT) and mutant yeast strains (as indicated) were added to nucleosomes reconstituted with radiolabeled 601 DNA and Xenopus laevis histone octamers and resolved on a 4% native polyacrylamide gels. Free nucleosomes are labeled N and nucleosomes bound by SWI/SNF as N-SWI. (E) The amount of bound nucleosomes versus SWI/SNF was determined from gel shift assays as shown in (B) and plotted. The estimated KD for wild type, Δsnf5 and Δswp82 SWI/SNF were 102 ± 19, 101 ± 15 and 82 ± 21 nM (standard deviation from mean), respectively, and were from three technical replicates.
