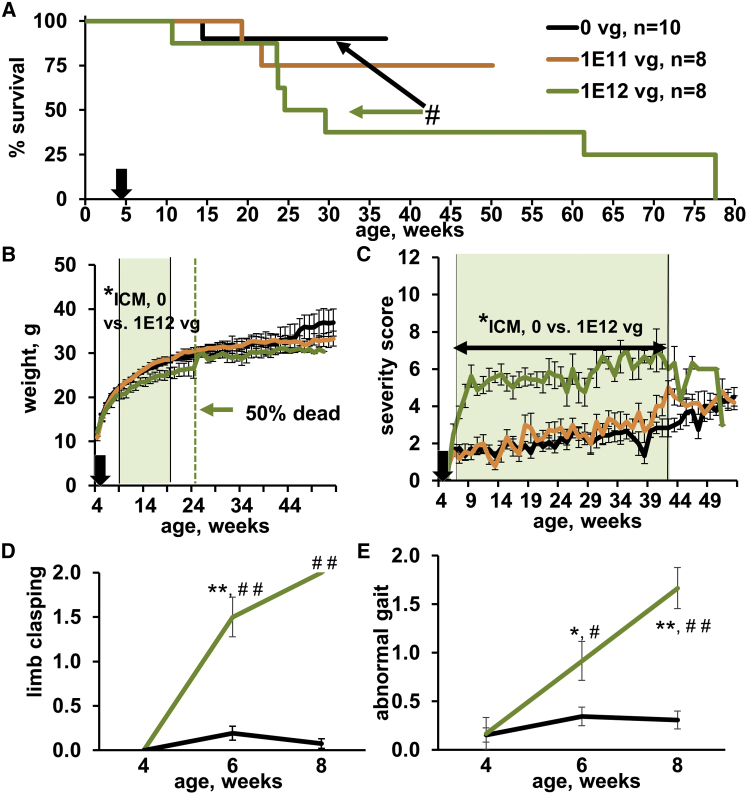
Figure 3.
ICM Delivery of AAV9/hMECP2(v1) Induces Behavioral Abnormalities in WT Mice
(A) AAV9/hMECP2(v1) shortens WT lifespan. Because WT and Mecp2−/y mice were tested in parallel, Figures 3 and 1 present the same data for saline-treated controls. #p = 0.04 (Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon test) for treated mice (WT, 1 × 1012 vg, ICM) versus controls (WT, 0 vg, ICM). (A–C) Injection time point is indicated by black arrows. (B and C) Shaded areas indicate times during which saline- and virus-treated cohorts had significantly different body weights or behavior scores; *p < 0.05. (B) 1 × 1012 vg (ICM) AAV9/hMECP2(v1) decreases body weight. Green dashed line at 25 weeks indicates the time point at which 50% of mice treated with 1 × 1012 vg AAV9/hMECP2(v1) (ICM) died. An increased mean weight for survivors is observed after this point. (C) In WT mice, 1 × 1012 vg AAV9/hMECP2(v1) induces behavioral abnormalities that are similar to those observed in Mecp2−/y mice (compare to Figure 1). Abnormalities persist until death. (D and E) AAV9/hMECP2(v1) (ICM) aggravates limb clasping and abnormal gait in WT mice. For clarity, only data for saline-treated and 1 × 1012 vg v1-treated mice are shown. p values (paired t test) for virus-treated WT mice versus their pre-treatment scores: **p = 0.001; *p = 0.04. p values (unpaired t test) comparing virus- and saline-treated mice at a fixed time point: ##p ≤ 0.0001; #p = 0.02. (B–E) Data points are mean ± SEM.