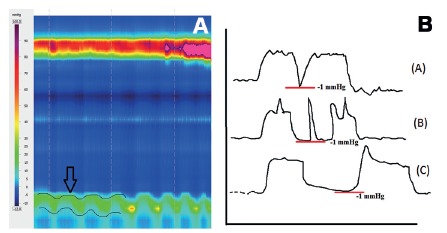
FIGURE 2. A) Lower esophageal sphincter respiratory oscillation: note that there is no dissociation of the components of the pressures corresponding to the diaphragm and lower esophageal sphincter, only respiratory motion (arrow); B) lower esophageal sphincter relaxation at conventional manometry measured by nadir pressure: pseudorelaxation due to factitious relaxation caused by sensor deeping into the stomach due to swallowing motion and not by actual relaxation of the sphincter; a short duration relaxation is noticed (A). In (B) diaphragmatic phasic contraction during relaxation may lead to misinterpretation of the relaxation duration, different from (C).