Figure 1.
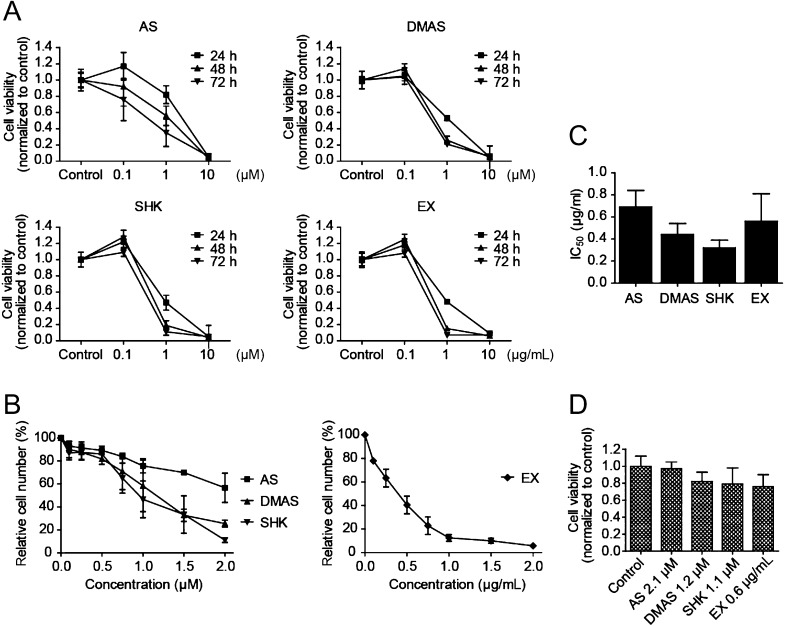
Shikonin derivatives inhibit proliferation of TT cells in a dose-dependent manner but do not reduce cell viability in normal human skin fibroblasts. (A) TT cells were incubated with 0.1, 1 and 10 µM acetylshikonin (AS), β,β-dimethylacrylshikonin (DMAS) or shikonin (SHK) and 0.1, 1 and 10 µg/mL petroleum ether extract of Onosma paniculata roots (EX). Cell viability was reduced at 1 µM concentrations of acetylshikonin, β,β-dimethylacrylshikonin and shikonin and 1 µg/mL of the extract. Concentrations of 10 µM and 10 µg/mL had deleterious effects on cell viability. Experiments were performed three times in sextuplicates. (B) Cell proliferation of TT cells as assessed by cell counting was dose dependently inhibited by acetylshikonin, β,β-dimethylacrylshikonin, shikonin and the extract. Cell numbers are presented as percentage of control solvent-treated cells, n = 3–4. (C) Conversion of determined IC50 values (Table 1) from µM to µg/mL allows comparison of potency between pure substances and the unfractionated extract. Shikonin and β,β-dimethylacrylshikonin were found to reduce cell proliferation at lower concentrations than the extract. (D) Cell viability of HF-SAR skin fibroblasts, on the contrary, was not significantly reduced when cells were incubated with the IC50 concentrations of shikonin derivatives determined for TT cells. Results were normalized to control solvent-treated cells, n = 3.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a