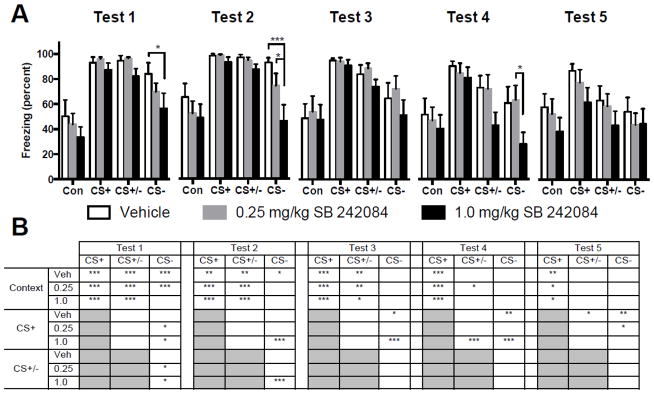
Figure 3.
A: Mean (+ SEM) percent time spent freezing during different cue conditions in recall tests 1 through 5. Systemic administration of the 5-HT2C receptor antagonist SB 242084 prior to fear discrimination conditioning facilitated CS+/CS− discrimination in recall tests 1 and 2, and facilitated conditioned inhibition (CS+ vs. CS+/−) on day 4. Brackets indicate significant differences between groups. B: Table summarizing significant comparisons between cues within each drug dose condition. Redundant pairwise comparisons are shaded in gray. In tests 1 through 5, regardless of drug conditions, freezing was significantly greater during presentation of the CS+ than to freezing in the context alone. However, in tests 1 and 2, the SB 242084 treated groups demonstrated discrimination with significantly less freezing during the CS− when compared to the CS+. In test 3, discrimination was evident in the vehicle treated groups with significantly less freezing to the CS− than to the CS+, and on day 5 conditioned inhibition was evident as less freezing during the CS+/CS− compound than to the CS+. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001