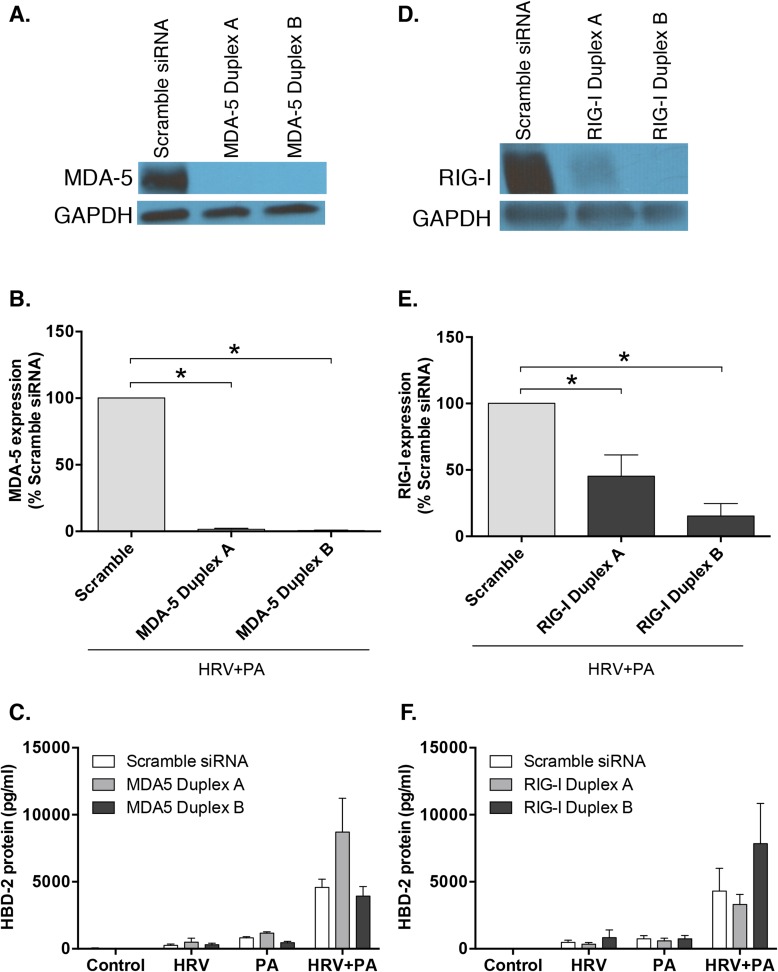
Fig 7. Limited reduction in human beta-defensin (HBD)-2 protein is seen following knockdown of retinoic-acid inducible gene (RIG)-I or melanoma differentiation associated gene-5 (MDA5).
A) MDA5 and D) RIG-I knockdown was assessed via western blot analysis of HBE cells co-infected with human rhinovirus (HRV)-16 and P. aeruginosa (PA) following lipid-mediated transfection (24 h) of 10 nM short-interfering RNA (siRNA) duplex A or B specific for MDA5, compared with non-targeting siRNA control. Densitometric analysis of B) MDA5 and E) RIG-I knockdown. HBD-2 protein levels were determined 48 h post infection with HRV-16, PA or the combination in the presence or absence of C) MDA5 siRNA duplex A or B (n = 4) or F) RIG-I siRNA duplex A or B (n = 3). Data expressed as mean ± SEM.