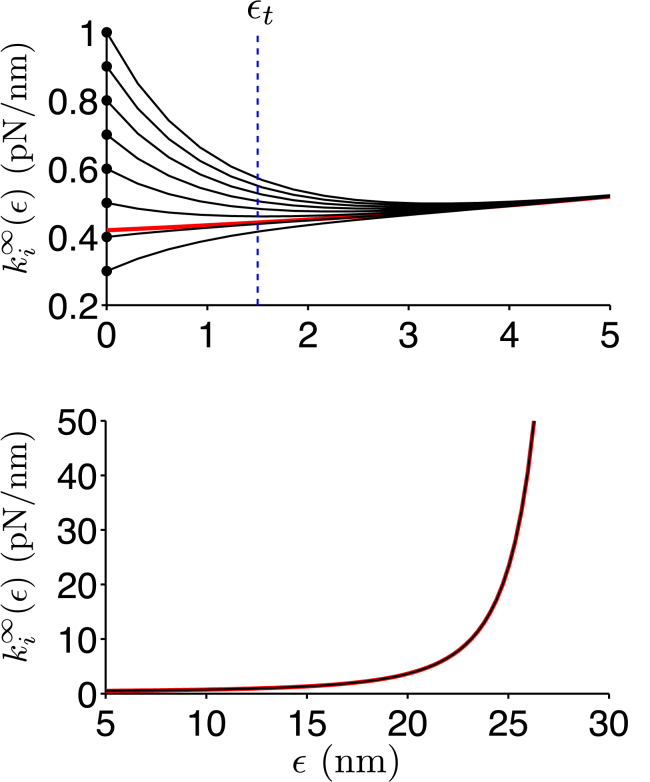
Figure 3.
Nonlinear spring stiffness for FN Type III domains. The steady-state spring stiffness values for the FN Type III domains ( in Eq. 7) are shown as a function of the domain stretch ϵ. (Top) In the absence of actomyosin forces and small domain stretch, each FN Type III domain spring constant k is equal to a unique spring constant ki,0 (Table S2), representing the unique mechanical properties of each FN Type III domain (black lines). (Bottom) In the presence of large actomyosin forces and large domain stretch, domain stiffness values are governed by a WLC model, producing a highly nonlinear increase in domain stiffness. (Red line) Domain binding site exposure threshold ϵt. (Dashed vertical blue line, top panel) To see this figure in color, go online.