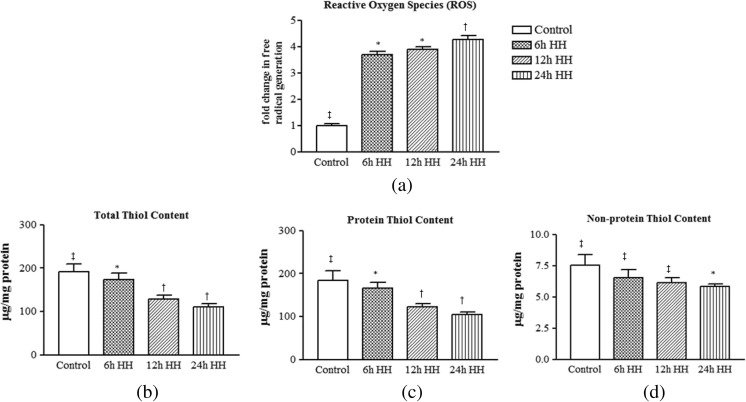
Fig. 1.
Hypobaric hypoxia induced oxidative damage via ROS generation and affects intracellular sulfhydryl content in rat muscle. a Reactive oxygen species. b Total thiol content (T-SH). c Protein thiol content (Pr-SH). d Non-protein thiol content (NPr-SH). Data represents the mean ± SE; N = 5. Different symbols, double dagger, asterisk, and dagger indicate the significant differences between experimental groups (p < 0.05), while groups with matching symbols denote no difference (p ≥ 0.05)