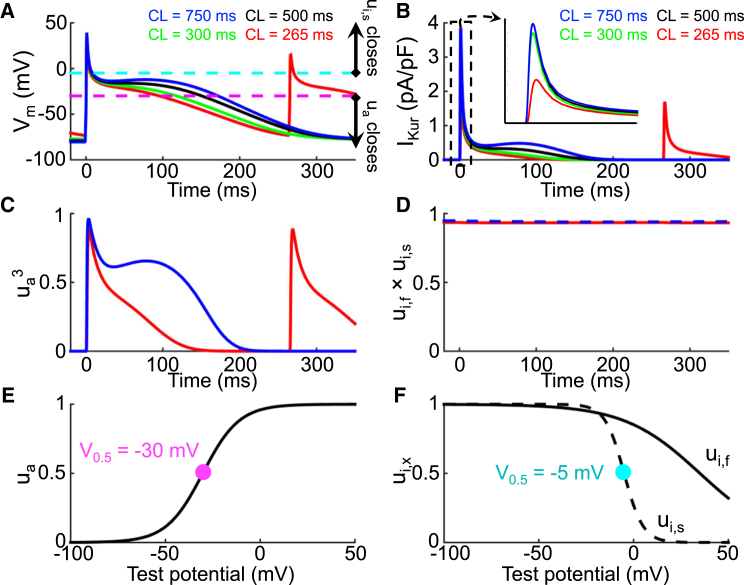
Figure 2.
Mechanism of IKur rate dependence. (A) Action potentials at stimulation cycle lengths from 265 ms (red), 300 ms (green), 500 ms (black), and 750 ms (blue) are shown. The purple and teal dashed lines correspond to the activation and inactivation gating variable 50% (V0.5,ua = −30 mV and V0.5,uis = −5 mV) opening potentials, respectively. (B) Shown here are corresponding IKur tracings; there is a rate-dependent decrease in IKur during phase 2 of the AP. (C) Shown here is the activation gate open probability (ua3) and (D) inactivation gate open probability (ui,f × ui,s) as a function of time for CLs of 265 ms (red) and 750 ms (blue). The activation open probability is rate dependent and the inactivation open probability is rate independent. (E) Shown here is the activation gating variable (ua) as a function of transmembrane potential; the purple dot corresponds to activation gating variable V0.5 as transposed on (A). (F) Fast (ui,f; black solid) and slow (ui,s; black dashed) inactivation gating variables as a function of transmembrane potential are given; the teal dot corresponds to the slow inactivation gating variable V0.5 as transposed on (A). The inactivation open probability is rate independent because the action potential spends very little time positive to V0.5,uis (−5 mV; teal).