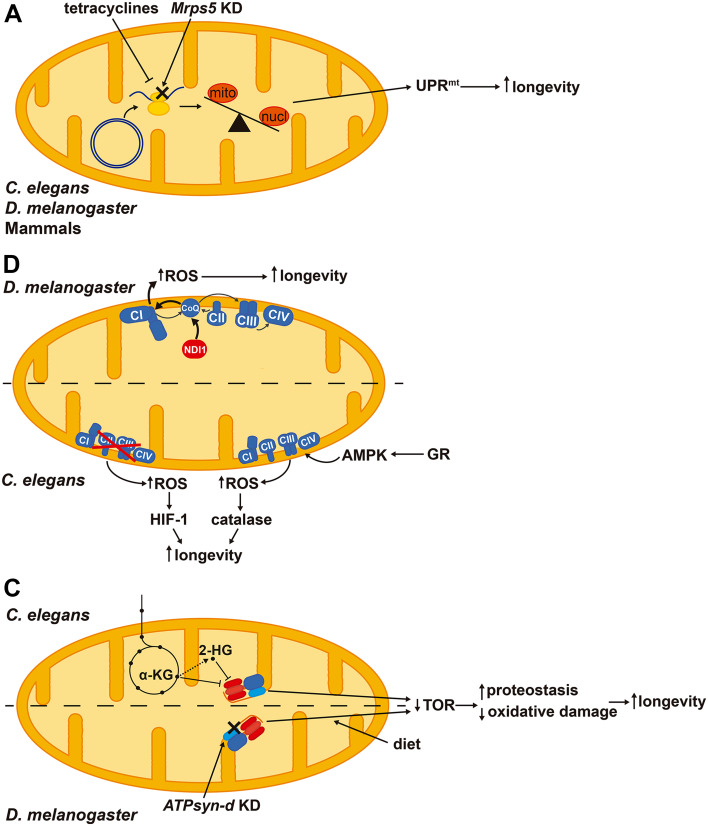
Fig. 5.
Signaling pathways that arise from mild mitochondrial stresses and contribute to lifespan extension in different model organisms. a Activation of the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) triggered by an imbalance between mitochondrial- and nuclear-encoded proteins extends longevity. b ROS derived from complex I (CI) by over-reduction of CoQ pool and reverse electron transport promote longevity in Drosophila melanogaster. Both reduction and enhancement of respiration in Caenorhabditis elegans trigger a ROS signal that promotes longevity via HIF-1 (hypoxia-inducible factor 1) or activating antioxidant defenses, respectively. c Inhibition of the H+-ATP synthase by α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) or 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) increases longevity through repressing TOR (target of rapamycin) signaling and improving proteostasis. Diet composition interacts with the knockdown (KD) of D. melanogaster H+-ATP synthase subunit d (ATPsyn-d) and TOR signaling in extending lifespan. Mrps5: mitochondrial ribosomal protein S5, GR: glucose restriction, AMPK: AMP-dependent protein kinase