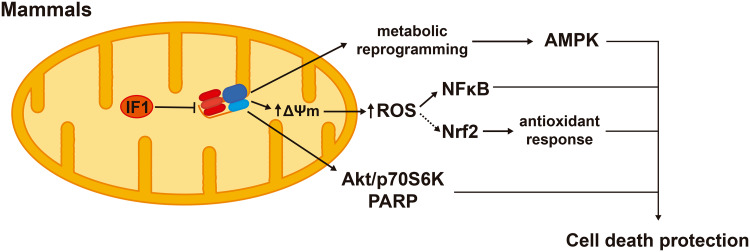
Fig. 6.
Signaling pathways modulated by IF1 that confer cell death protection. IF1-mediated inhibition of the H+-ATP synthase triggers metabolic reprogramming to an enhanced glycolysis and the activation of AMPK (AMP-dependent protein kinase). IF1 inhibition of the synthase also increases ROS production and the ROS-dependent activation of NFκB (nuclear factor kappa B). ROS might also mediate the enhanced Nrf2 [nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2]-guided response that prevents oxidative damage. In neurons, IF1 inhibition of the H+-ATP synthase activates Akt (AKT serine/threonine kinase), p70S6K (ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 70 kDa) and PARP (poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase) survival and repair pathways