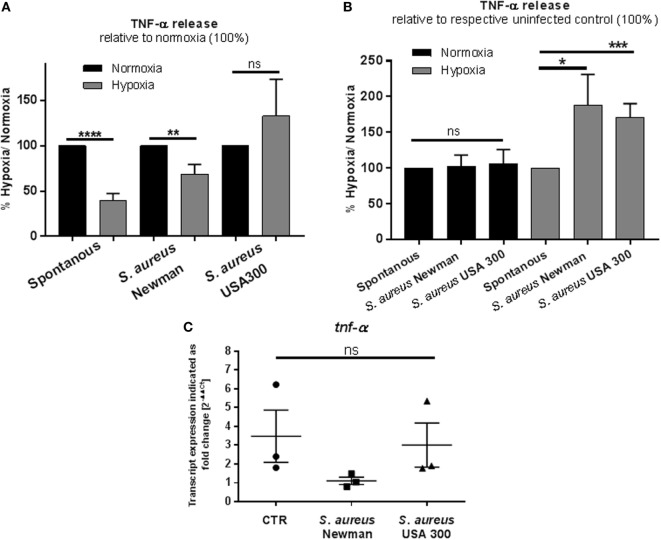
Figure 4.
TNF-α: release and transcript expression. (A) TNF-α release of 1 × 106 cell/ml was measured by a TNF-α ELISA (murine TNF-α ELISA development kit, PeproTech). Mast cells (MCs) were preincubated under hypoxia/normoxia for 3 h and infected with h.i. Staphylococcus aureus Newman/USA 300 at a MOI of 1 for 45 min. Comparing the release to the normoxic control (set to 100%), spontaneous and S. aureus Newman-induced TNF-α release is decreased under hypoxia (n = 3 independent experiments measured in triplicates). (B) TNF-α release in comparison to the untreated control (spontaneous release). The spontaneous release is set to 100% and compared to S. aureus-induced TNF-α release under the respective oxygen control. In comparison to its control, TNF-α release is not altered under normoxia. Under hypoxia, significantly more TNF-α is released, when stimulated with S. aureus Newman as well as USA 300 (n = 3 independent experiments measured in triplicates). (C) Transcript expression of tnf-α under hypoxia compared to normoxia (n = 3 independent experiments, all PCR runs were performed twice, depicted are the means of each run). MCs were incubated under hypoxia or normoxia for 3 h and incubated with h.i. S. aureus Newman/USA 300 at a MOI of 1 for 45 min before RNA was isolated. Data were normalized to the non-regulated housekeeping gene rps9. The x-fold changes of the values from samples incubated under hypoxia were calculated against the normoxic samples. The spontaneous tnf-α gene expression under hypoxia compared to normoxia is increased. Comparing the expression of tnf-α in response to S. aureus Newman, this induction phenomenon is abolished; the expression is decreased significantly in comparison to the spontaneous expression. No differences are observed for S. aureus USA 300-induced tnf-α expression.