Figure 5.
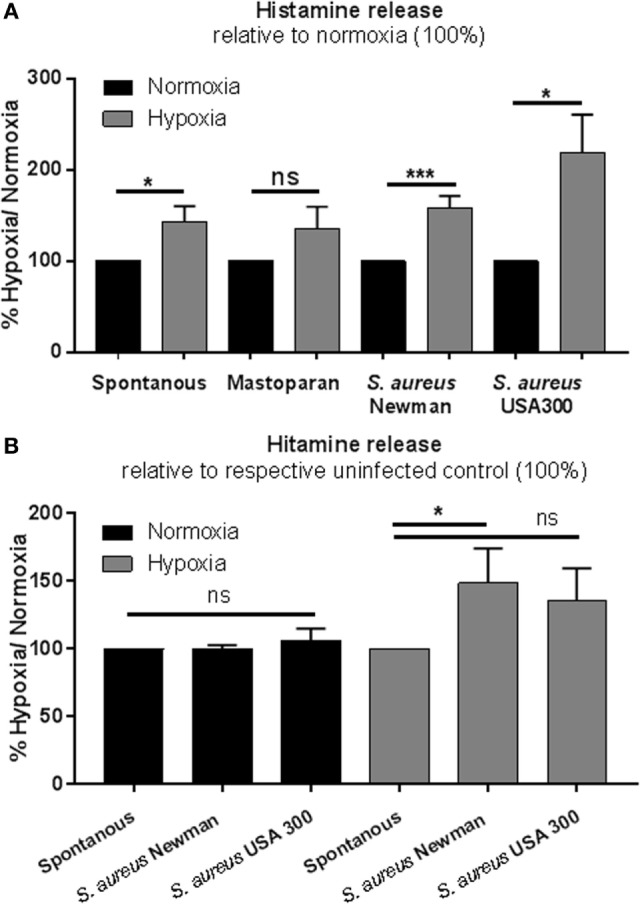
Histamine release. (A) Histamine release of 1 × 106 cell/ml was measured by rpHPLC (n = 3 independent experiments measured in duplicates). Mast cells (MCs) were preincubated under hypoxia/normoxia for 3 h and incubated with a MOI 1 h.i. Staphylococcus aureus Newman and h.i. S. aureus USA 300, stimulated as a positive control with the MC-degranulating peptide mastoparan (50 μM Bachem, Heidelberg, Germany), and HBSS (spontaneous release) for 45 min. Comparing the release to the normoxic control (set to 100%), spontaneous S. aureus Newman and S. aureus USA 300-induced histamine release is increased under hypoxia. No differences in mastoparan-induced histamine release are observed between hypoxic and normoxic conditions. (B) Histamine release comparing the spontaneous release (set to 100%) and the S. aureus-induced histamine release under normoxic and hypoxic conditions (n = 3 independent experiments measured in duplicates). Histamine release under normoxia is not altered by S. aureus. Under hypoxia, significantly more histamine is released, when stimulated with S. aureus (significant for S. aureus Newman).
