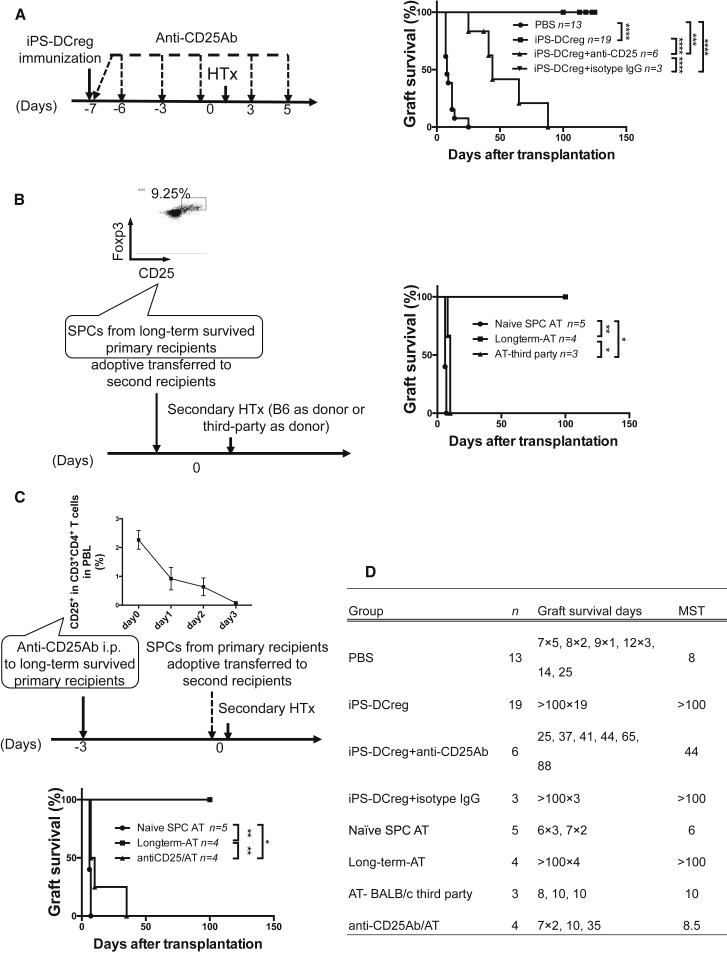
Figure 5.
Tregs Generated by iPS-DCreg Immunization Are Donor Specific and Play a Key Role in Tolerance Induction and Maintenance
(A) CBA recipient mice were treated with B6 iPS-DCregs and anti-CD25 mAb. A statistical evaluation of graft survival was performed using Kaplan-Meier curves and compared using log-rank tests. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
(B) SPCs harvested from iPS-DCregs-treated recipients (primary recipients) on POD100, which included 9.25% Tregs in the CD4+ population, were adoptively transferred to naive CBA (secondary recipients) at 5 × 107, and B6 hearts or BALB/c hearts (third party) were transplanted into the second recipients. A statistical evaluation of graft survival was performed using Kaplan-Meier curves and compared using log-rank tests. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.
(C) Anti-CD25 mAb was injected into the primary recipients on POD97. The depletion of CD25+ cells was monitored in peripheral blood (PBL) by FCM. SPCs were then isolated from the primary recipients on POD100 and adoptively transferred to naive CBA (secondary recipients) at 5 × 107 just before the second transplantation. A statistical evaluation of graft survival was performed using Kaplan-Meier curves and compared using log-rank tests. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.
(D) Graft survival data in this figure are presented in detail.