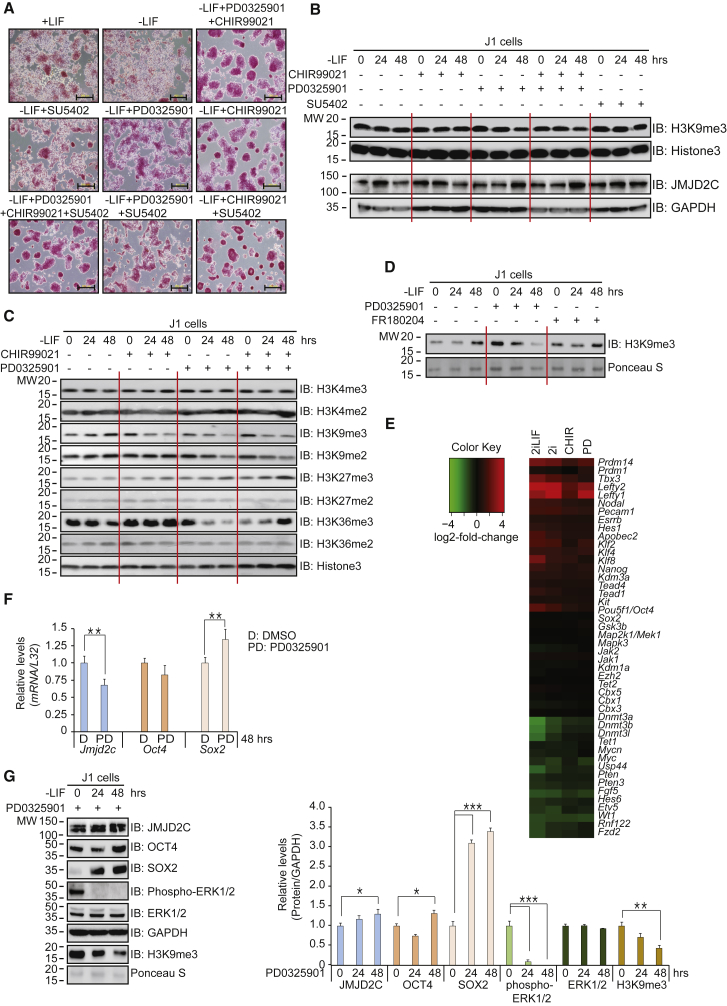
Figure 1.
MEK Inhibition Regulates JMJD2C Stabilization and Decreases H3K9me3 Levels
(A) AP staining shows that combinatorial treatments of three small-molecule inhibitors induce pluripotency in ESCs. Scale bar, 200 μm.
(B) Western blots show that PD0325901 increases JMJD2C protein levels and decreases H3K9me3 levels. ESCs were cultured in feeder-free and LIF-free conditions with inhibitors for 24 and 48 hr.
(C) PD0325901 and/or CHIR99021 induce changes of histone H3 methylation in feeder-free and LIF-free ESCs.
(D) MEKi with PD0325901 decreases H3K9me3 levels in ESCs, but not ERKi with FR180204 in western blots.
(E) Combinatorial 2i treatments change gene expression in ESCs. Data come from the GEO DataSet (GEO: GSE43597). The 2i treatments upregulate Prdm14 and downregulate the Dnmt3 family.
(F) qRT-PCR (n = 4 independent experiments) shows that PD0325901 decreases Jmjd2c mRNA levels compared with the DMSO control.
(G) Western blots show that PD0325901 increases JMJD2C, OCT4, and SOX2 protein levels but decreases H3K9me3 levels (n = 3 independent experiments).
∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.